Why Do I Feel Sick Every Time I Eat? (8 Commonest Causes).
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
Feeling sick after eating can be due to either stomach conditions or medication.
Common causes of feeling sick every time you eat include gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, GERD, functional dyspepsia, food intolerances, and some medications.
Here is a breakdown of the cause of feeling sick every time you eat:
- Chronic gastritis.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or chronic acid reflux.
- Food intolerances or allergies.
- Gastroparesis (lazy stomach).
- Acute gastroenteritis or acute gastritis.
- Some medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Chronic stress and anxiety.
- Others such as gallstone disease, chronic pancreatitis, pregnancy, premenstrual syndrome, etc.
Table of Contents
1. Chronic gastritis & PUD.
Inflammation of the wall of your stomach is called gastritis. It is one of the most common diseases. The two main causes of gastritis are (reference:
- Overuse of pain medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs).
- Infections with an organism called (H. pylori).
Patients with gastritis or gastric ulcers commonly feel sick every time they eat. Gastritis is one of the diseases that are affected by what you eat.
Many foods and drinks may trigger the symptoms of gastritis. So, stomach inflammation (gastritis) or ulcers (peptic ulcers) are the first things to consider if you become sick every time you eat.
Eventually, the chronic inflammation may lead to a profound injury of the stomach wall with a breakdown of its lining.
The breakdown of the stomach lining is called gastric peptic ulcer. At some point, the peptic ulcer may bleed and lead to vomiting of blood (hematemesis) or passage of black stool (melena) (reference).
Symptoms:
- Pain: persistent or recurrent pain in the upper central part of the abdomen (epigastric area). The pain is often burning or gnawing in nature.
- Meal-related: the pain in patients with chronic gastritis is typically related to meals.
- Sick feeling: The sick feeling (nausea) often occurs every time you eat. The nausea is more with certain trigger foods (mentioned below).
- Vomiting in some patients.
- Anorexia (poor appetite or lack of appetite).
- Sometimes, the epigastric pain is minimal, and the main complaint of the patients is the sick feeling every time they eat.
- Bleeding peptic ulcers may cause vomiting of blood (hematemesis) or passage of black stool (melena).
- Risk factors are often present, such as:
- H. pylori infection.
- NSAIDs overuse.
- Smoking.
- Alcohol overuse.
- Physical inactivity.
Most common foods that trigger gastritis symptoms:
- Caffeine in coffee and other caffeinated drinks and chocolate.
- Spicy foods.
- Alcohol
- Fatty and fried foods
- Citrus fruits.
- Carbonated (soft) drinks.
- Tomatoes and tomato products such as ketchup and sauce.
Learn more about the foods that trigger gastritis.
How gastritis is diagnosed:
Your doctor usually needs to perform endoscopy and/or H. pylori testing to diagnose gastritis. Also, he may take a biopsy of the stomach wall to confirm the diagnosis.
2. GERD (acid reflux).
GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) or chronic acid reflux is a common condition resulting from the regurgitation of stomach acid into the esophagus.
GERD is one of the most common diseases in the USA and worldwide. According to this review study, Up to 20% of the western world suffers from GERD.
GERD occurs due to abnormalities in the sphincter between the esophagus and the stomach or herniation of a part of your intestine to the chest through the diaphragm (hiatal hernia).
Every time you eat, the food & acid in your stomach may reflux back to the esophagus and cause symptoms, including a sick feeling after eating.
Symptoms of GERD (reference):
- Heartburn: burning sensation and a sick feeling in the chest. It typically occurs every time you eat and at night.
- Regurgitation: of acidic fluid or food particles into your throat.
- Nausea (sick feeling) every time you eat).
- Chocking attacks: these often occur at night during sleep time. It may be so severe with persistent cough and vomiting.
- Chest pain.
- Increased salivation.
- Globus (foreign body) sensation in your throat.
The sick feeling is often triggered by eating large meals or sleeping immediately after eating.
How GERD is diagnosed:
Your doctor can diagnose GERD based on clinical symptoms only if you have the typical symptoms. Also, he may need to perform an endoscopy to confirm the condition.
3. Functional dyspepsia (Indigestion).
5 to 11% of people worldwide have functional dyspepsia (indigestion) (reference). Dyspepsia is an uncomfortable feeling in the upper stomach (often occurs every time you eat).
The most common cause of dyspepsia is gastritis and peptic ulcer disease.
However, many people may suffer from dyspepsia or sick feeling without gastritis or any other cause. This type of idiopathic dyspepsia is called (functional dyspepsia).
The sick feeling every time you eat with discomfort in your upper stomach may result from functional dyspepsia.
Symptoms:
- Uncomfortable feeling in the epigastric area after eating.
- Fullness after eating is the most common symptom of functional dyspepsia.
- Early satiety.
- Nausea or sick feeling every time you eat.
- Mild to moderate epigastric pain or burning sensation.
Learn more about functional dyspepsia and how it is diagnosed HERE.
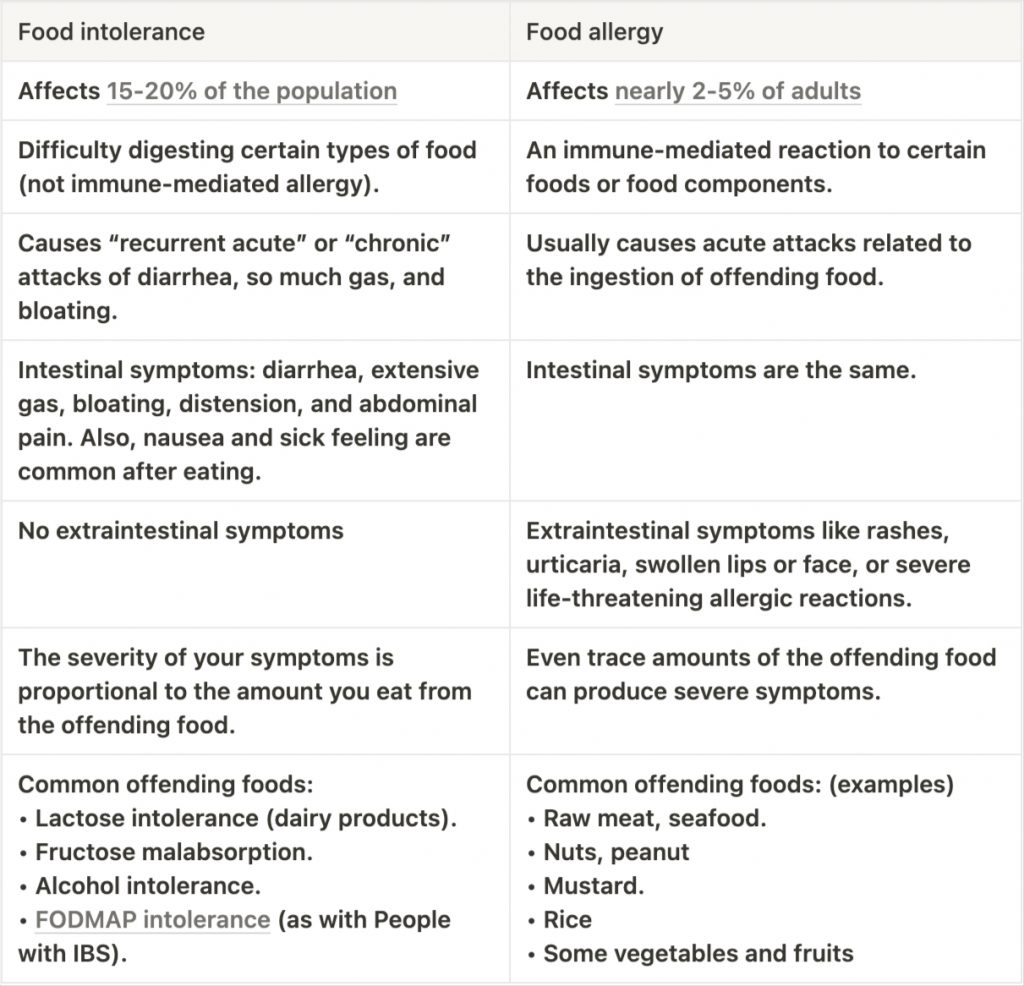
4. Food intolerances & allergies.
Your digestive system may find difficulty digesting certain foods or food constituents.
For example, adults may lose their ability to digest the lactose sugar found in milk and dairy products as they grow up. This condition is called lactose intolerance.
As a result, you may experience a sick feeling every time you eat the offending food.
On the other hand, a food allergy is a different form of food reaction.
Unlike food intolerance, food allergy is not just a difficulty digesting food; it is an immune-mediated allergic reaction to certain foods that may cause allergic symptoms such as skin rashes.
Both food allergies and food intolerances can make you feel sick every time you eat.
The table below explains food intolerances and allergies (similarities, differences, and examples):
5. Acute gastritis/gastroenteritis.
The recent onset of severe watery diarrhea, stomach upset (sick feeling), and indigestion is commonly due to infections of your gastrointestinal tract. The most common cause of infection is viral gastroenteritis (stomach flu).
Viral gastroenteritis or stomach flu starts as sudden diarrhea, abdominal pain, indigestion, nausea, and vomiting.
Causes of acute gastroenteritis:
- Viral gastroenteritis (commonest): such as norovirus, rotavirus, etc.
- Bacterial gastroenteritis (most severe) includes E. Coli, Shigella, etc.
- Protozoal infections such as amoebiasis and giardiasis.
Symptoms of acute gastroenteritis include:
- Acute onset abdominal pain or discomfort.Acute onset diarrhea (usually watery and yellowish).
- Nausea and maybe vomiting.
- Indigestion (dyspepsia) and a sick feeling every time you eat.
- Fever (often very mild or low-grade). However, bacterial gastroenteritis may cause high-grade fever.
- Body aches and fatigue.
- Headaches.Anorexia (loss of appetite).
- The symptoms of acute viral gastroenteritis typically last for one to 3 days and then resolve spontaneously.
6. Gastroparesis (common in diabetes mellitus).
Gastroparesis is a condition that affects the normal spontaneous movement of your stomach. With gastroparesis, your stomach slows down, resulting in food staying longer inside your stomach.
Patients with gastroparesis often feel sick and full for several hours every time they eat.
Bloating after eating minimal amounts of food is also common with gastroparesis. The difference between gastroparesis and functional dyspepsia is:
The most common cause of gastroparesis is diabetes mellitus. Diabetes may cause damage to the nerves supplying the stomach (vagus nerve), affecting its motility.
Other causes and risk factors (reference):
- Abdominal or esophageal surgery.
- Infection, stomach viruses.
- Certain medications, such as pain medications.
- Nervous system diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis.
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid).
- Scleroderma (a connective tissue disease).
Learn more about gastroparesis HERE.
7. Medications.
Medication is a common cause of a sick feeling or nausea every time you eat. The table below includes the most common medications that cause nausea after eating.
Review your list of medications and supplements for any of the below drugs (reference).
| Medications causing nausea | Examples |
|---|---|
| 1- Analgesics: medications used to treat headaches and pain | Aspirin.Other NSAIDs such as Ibuprofen, ketoprofen.Anti-gout medications. |
| 2- Drugs for heart diseases: | Digoxin (especially over-dose).Beta-blockers (such as bisoprolol).Calcium channel blockers (as Amlodipine).Other antihypertensives and anti-arrhythmia medications.Diuretics |
| 3- overuse of vitamin supplements (hypervitaminosis). | Vitamin D overdose.Vitamin A overdose. |
| 4- Cancer chemotherapy. | Severe nausea and vomiting, especially with: Cisplatinum.Dacarbazine.Nitrogen mustard. Others cause moderate to mild nausea: Methotrexate.Cytarabine.Etoposide.Fluorouracil.Tamoxifen. |
| 5- Hormonal preparations/therapies | Oral contraceptives.Anti-diabetic drugs. |
| 6- Antibiotics / Antivirals | Erythromycin.Tetracycline.SulfonamidesAnti-TB drugs.Acyclovir. |
| 7- IBD (Crohn’s & Ulcerative Colitis) medications | Sulfasalazine.Azathioprine. |
| 8- CNS drugs: | Antiparkinsonian drugs.Anticonvulsants (& epilepsy) drugs. |
| 9- Anti-asthma drugs: | Theophylline |
8. Irritable bowel syndrome, stress, & anxiety.
Irritable bowel syndrome is a very common functional bowel disorder that affects nearly 15% of people worldwide.
It is commonly related to stress and anxiety, and females are more commonly affected by IBS than men.
Patients with IBS often suffer from recurrent abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits (constipation or diarrhea).
In addition, IBS patients may feel sick every time they eat, as food is one of the most recognized triggers of IBS.
Learn more about IBS and appetite changes.
9. Others (less common).
- Celiac disease.
- Gallbladder stones and chronic cholecystitis.
- Chronic pancreatitis.
- GI cancers
- chronic mesenteric ischemia.
- Pregnancy.
- Hormonal disturbances in females.
- Chronic diseases.
- Acute and/or chronic pain.
- Chronic migraine.
- Ear problems.
- Neurological diseases: Anorexia Nervosa, parkinsonism, increased intracranial tension, brain tumors, etc.
- And others. Learn More.
When to see a doctor (when to worry)?
See a doctor if you have the following:
- Persistent nausea or sick feeling for several days or months without obvious cause.
- Persistent vomiting.
- Severe epigastric pain or heartburn.
- Fever.
- Vomiting of blood.
- Black stools.
- Persistent diarrhea.
- Significant loss of weight.
- Taking any medications that cause nausea or gastritis.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.












