Yellow Diarrhea Every 10 Minutes: 3 Main Causes & When to Worry.
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
The most common cause of yellow watery diarrhea every 10 minutes is acute gastroenteritis (viral, bacterial, or protozoal). Very frequent watery yellow may lead to dehydration and complication if prolonged.
If you are getting diarrhea every 10 minutes, it often will improve gradually. However, it may lead to complications such as severe dehydration, especially in infants, older people, and people with chronic debilitating diseases.
Often consult your doctor if extreme diarrhea lasts for more than 3-5 hours without signs of improvement.
Today, you will learn about the most likely causes of acute frequent, non-stop diarrhea.
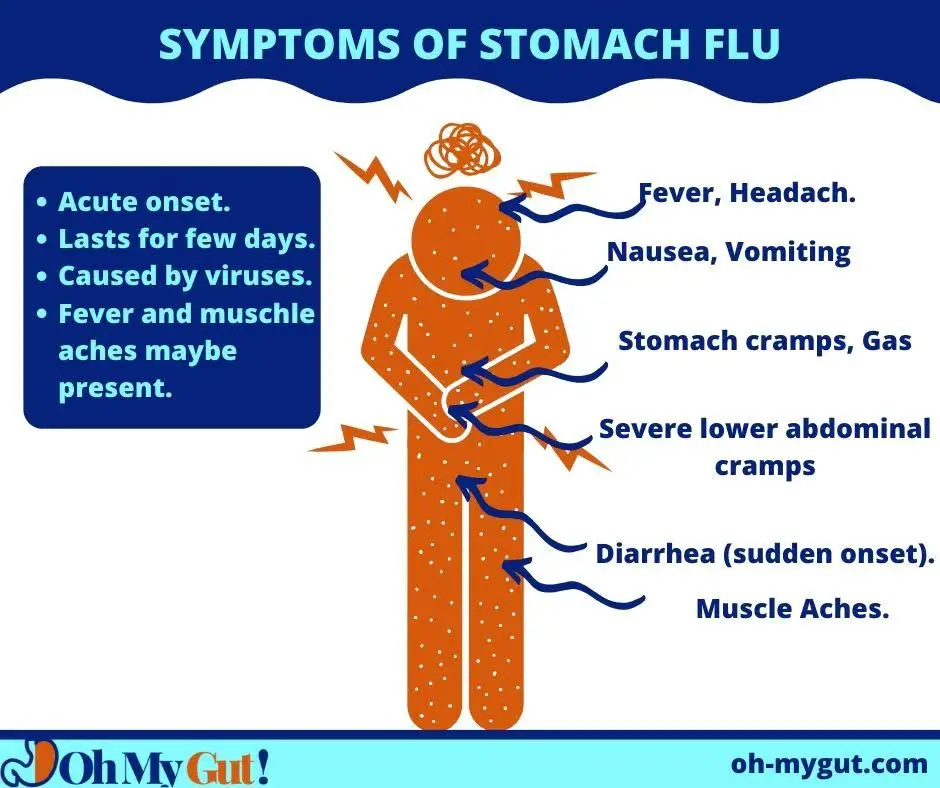
1. Stomach Flu (viral gastroenteritis).
Stomach flu or viral gastroenteritis is the most common cause of gastroenteritis. For example, Norovirus infection represents nearly 60% of all cases of acute gastroenteritis.
These viruses are often acquired from an infected person (who sheds the virus with his stool or vomits). Viral gastroenteritis typically causes short-term illness (a day or two), severe diarrhea (every 10 to 120 minutes), and vomiting.
Causative organisms:
- Norovirus (the most common cause of acute viral gastroenteritis).
- Rotavirus (less prevalent nowadays due to the introduction of the rotavirus vaccine).
- Enteric adenovirus.
- Astrovirus.
How Do you get stomach flu:
- Eating food or drinks contaminated with stomach viruses.
- Close contact with an infected person.
- Using the personal utensils of an infected person.
- The symptoms of norovirus often start 24-48 hours after acquiring the infection.
Symptoms:
- The symptoms start acutely with sudden diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting.
- Vomiting is present in more than 50% of the cases.
- Diarrhea is often moderate, but it can be severe (every 10 minutes).
- Abdominal cramps.
- Bloating.
- Severe anorexia (loss of appetite).
- Muscle aches.
- Fever is either absent or low grade.
- Significant muscle and joint pain.
- Fatigue.
- Typically, severe diarrhea lasts from 12 to 60 hours (36 hours on average).
- In severe cases, dehydration symptoms may develop such as:
- Extreme thirst.
- Dry mouth.
- Dry tears.
- Cold, clammy extremities.
- Dizziness, lightheadedness.
- Fast heartbeats.
- Shortness of breath.
- Fainting.
- Dehydration and complications are more common in age extremities (children and elderly over 60 years). Also, in people with severe debilitating diseases such as kidney failure, heart failure, liver cirrhosis, etc.
What to do:
- See a doctor if you have signs of dehydration, severely debilitating disease, or high-grade fever.
- In most cases of acute gastroenteritis, severe diarrhea every few minutes will last a few hours, then gradually improve.
- Meanwhile, it would help if you stay hydrated (sip small amounts of water every few minutes).
- If there is recurrent vomiting, try to stop eating for a few hours to let your stomach settle.
- Foods that fight watery diarrhea include bananas, rice, apple sauce, and toast (BRAT diet).
- Foods to avoid include high-fat, fried, and spicy foods.
- Eating smaller, lighter, more frequent meals is better than a large meal.
- Loperamide is an OTC anti-diarrheal that helps stop severe diarrhea with GE. The dose of loperamide (Immodium A-D®) is one caplet first, then one caplet after every diarrhea attack (but no more than four caplets a day).
- Stomach flu is a viral infection. So, antibiotics (antibacterial agents) have no role in viral gastroenteritis.
- Also, Pepto-bismol is another good option.
2. Bacterial GE, Food poisoning, and other infections.
Bacteria are a less common cause of gastroenteritis. However, bacterial gastroenteritis is usually more severe and can cause more severe forms of diarrhea (every 10 minutes).
Causative organisms of food poisoning:
- Staph. Aureus.
- Campylobacter Jeujeni.
- Shigella species (commonly cause bacillary dysentery).
- Salmonella species.
- Yersinia.
- E. coli.
- Other parasites such as cryptosporidium.
- Viruses alo
How do you get food poisoning?
The most common route is eating foods or fluids contaminated by bacteria or toxins.
The table below illustrates the most common causes and their incubation periods (periods between acquiring the infection and the appearance of symptoms):
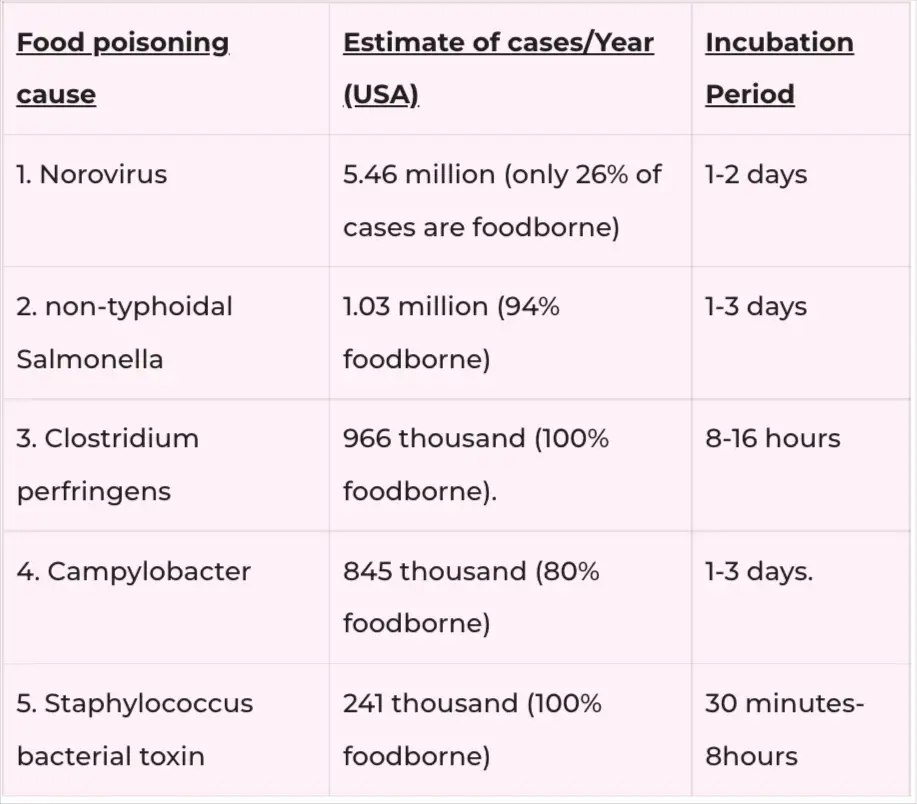
Symptoms of bacterial GE/food poisoning:
The table below illustrates the main differences between stomach flu (viral GE) and other types of GE (Especially bacteria GE).
| TYPE | VIRAL GE | FOOD POISONING |
|---|---|---|
| CAUSE | Viruses such as norovirus and rotavirus | Eating food contaminated with bacteria, viruses, or Protozoa. |
| Site of infection | Affects the stomach and small intestine. | Affects the colon mainly. |
| Diarrhea type. | Moderate or mild. | Moderate to severe (more likely to cause diarrhea every 10 minutes. |
| Vomiting | Usually present | Usually present. Severe with certain types of food poisoning. |
| Diarrhea color | often yellow. | Often yellow but may contain mucus and blood. |
| Body aches | Common | Less common |
| Cramps. | moderate | severe |
| Fever | low grade. | High-grade. |
| Anorexia | Mild to moderate | Severe |
| Complications | less common | Common. |
| Duration | usually 1-3 days | Usually 1-10 days. |
3. Giardiasis.
Giardiasis is a protozoal infection famous for causing severe acute yellow watery diarrhea.
Giardiasis diarrhea is more common in travelers, children, and young infants.
You acquire giardiasis by eating or drinking contaminated food or water or contacting an infected person.
Symptoms:
- The symptoms are in the form of gastroenteritis (severe diarrhea, malaise, cramps, etc.)
- Giardiasis is famous for yellow diarrhea as it leads to fat malabsorption.
- Also, the organism causes significant weight loss secondary to fat malabsorption.
- The stool is often yellow, foul-smelling (more fat), and watery.
- It can be very severe (every 10 minutes), but constipation also can occur.
- The symptoms are more prolonged (one to four weeks) and may turn chronic.
The symptoms of acute giardiasis (and their frequency are illustrated in the table below (reference):
| SYMPTOM | FREQUENCY. |
|---|---|
| Diarrhea | 90% |
| Malaise | 86% |
| Foul-smelling, yellow watery stool (fatty) | 75% |
| Abdominal cramps, bloating | 71% |
| Flatulence | 75% |
| Nausea | 69% |
| Weight loss | 66% |
| Vomiting | 23% |
| Fever | 15% |
| Constipation | 13% |
| Urticaria. | 10% |
4. Other causes of yellow diarrhea every 10 minutes (less common).
- Antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
- Laxative overuse or overdose.
- Severe anxiety or stress.
- Cholera (rice-watery whitish diarrhea, no yellow).
- Poisoning (such as lead poisoning & other heavy metals).
- Alcohol overuse.
- Organophosphorus poisoning (insecticides).
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease).
- Ischemic colitis.
- Early appendicitis (often associated with severe lower abdominal pain on the right side or around the umbilicus).
- An attack of irritable bowel syndrome.
- An attack of food allergy or food intolerance.
When to see a doctor.
- Severe, frequent diarrhea (every 10 to 30 minutes) for more than 3-5 hours non-stop.
- Signs of severe dehydration such as extreme thirst, peeing too little urine, fast heartbeats, dry mouth, dryness of tears, confusion, dizziness, fainting, etc.
- Blood in the stool.
- Fever >38.5°C or 101.3°F.
- Severe intolerable abdominal pain.
- Infants and elderly over 70 years.
- Serious comorbid diseases such as Heart diseases, Impaired immunity (as with HIV patients), kidney disease, liver cirrhosis, etc.
- Pregnancy.
- Severe vomiting.
- Confusion, dizziness.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.







