Non-stop Diarrhea: Causes & Treatment, Gastroenterologist explains.
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
Causes of acute non-stop diarrhea.
The most common cause of acute non-stop diarrhea is gut bugs. An infection with a virus, bacteria, or parasites leads to acute diarrhea.
Viral gastroenteritis tends to be milder than bacterial causes. Viruses are the most frequent cause of acute infectious diarrhea.
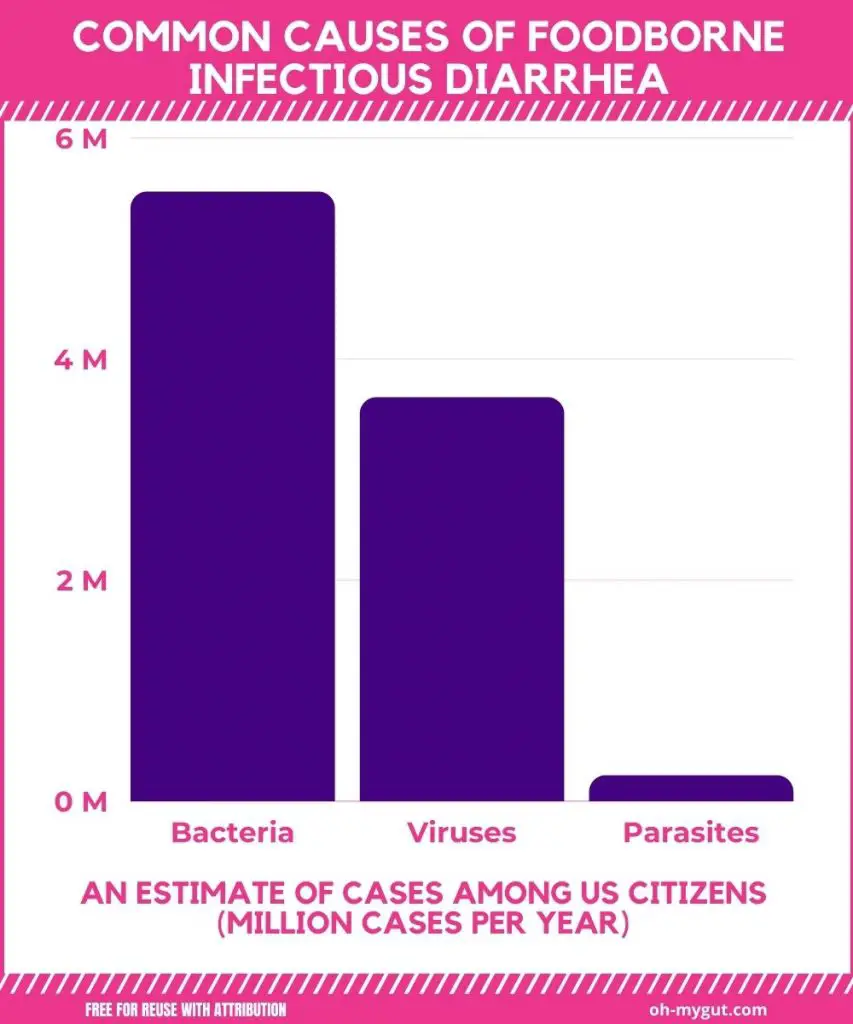
The frequency of acute diarrhea(based on the 2006 US population) is (reference):
- Viral gastroenteritis: about 5.51 million cases per year.
- Bacterial gastroenteritis: 3.56 Million cases per year.
- Parasitic gastroenteritis: about 233,000 cases per year.
You get infected by:
- Eating contaminated foods or drinks.
- Traveling to an endemic area.
- Contacting an infected person.
Also, Non-infectious causes of acute diarrhea can lead to non-stop diarrhea. Examples, Drugs, acute attacks of IBS, and an attack of food intolerance or allergy (see below).
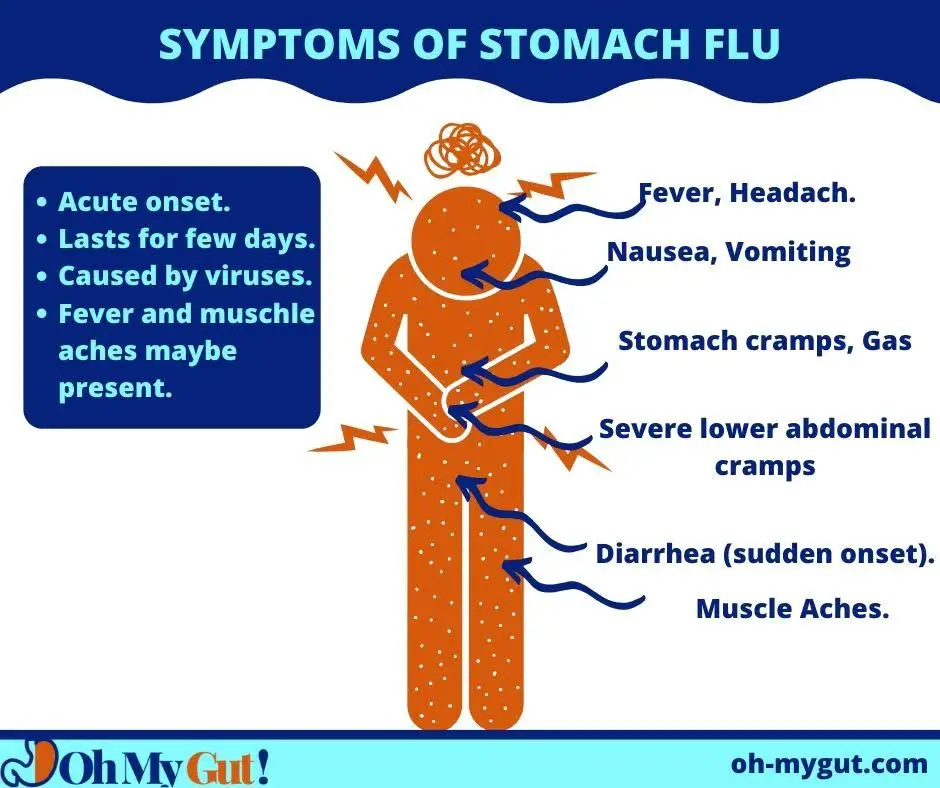
1. Acute Viral Gastroenteritis.
Acute viral gastroenteritis is also called stomach flu. It is the most common cause of acute infectious diarrhea.
The most common causes are Rotavirus and norovirus. Rotavirus is the most common cause of viral gastroenteritis worldwide (reference). However, Introducing the rota vaccine (as in the USA) made the virus less prevalent.
Symptoms:
- Acute onset of severe non-stop diarrhea (usually watery and yellow).
- Diarrhea usually lasts a few days (2-5 days) but may last longer.
- Abdominal cramps (usually at the lower abdomen).
- Anorexia (loss of appetite).
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Fever is usually present (often of low grade). The fever may be unnoticeable (only a cold sensation or sense of fatigue or muscle aches).
2. Bacterial Gastroenteritis.
Bacteria leads to a more severe form of diarrhea. The most prevalent organisms that cause bacterial gastroenteritis include (reference):
- Salmonella species (typhoid fever).
- Clostridium perfringens (foodborne).
- Campylobacter species.
- Staphylococcal aureus (foodborne).
- E. Coli species.
Most cases of bacterial gastroenteritis (GE) are foodborne. Bacterial gastroenteritis is the most frequent cause of food poisoning.
The symptoms are typically more severe than viral gastroenteritis:
- The diarrhea is severe, non-stop.
- Bloody and mucoid diarrhea are common.
- Tenesmus (an urge to poop, but only mucus or scanty stool comes out).
- Fever is high grade.
- Vomiting is more common and severe.
- More severe systemic illness (headache, fatigue, muscle aches, and dizziness).
3. Protozoal & other types of gastroenteritis.
Parasites can also cause severe forms of non-stop diarrhea. The most common organisms are:
- Toxoplasma gondii.
- Giardiasis
- Cryptosporidium species.
- Entamoeba Histolytica (causes dysentery rather than diarrhea).
The symptoms of protozoal infections are similar to that of viral diarrhea. Giardiasis can cause a severe form of non-stop diarrhea. It can cause fat malabsorption, yellow diarrhea, fever, and vomiting. Learn More.
4. Other causes of acute non-stop diarrhea.
Infections are not the only cause of acute non-stop diarrhea. Other causes include:
- Taking medications that cause diarrhea, such as antibiotics, laxatives, and others. Learn more.
- An attack of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS flare-up).
- An acute attack of food intolerance or allergy following ingestion of the offending food (such as dairy, alcohol, and caffeine).
Causes of chronic non-stop diarrhea.
Non-stop diarrhea can turn chronic. It lasts for more than four weeks. Chronic nonstop diarrhea can be due to (reference):
- Celiac disease: chronic non-stop diarrhea and bloating due to gluten intolerance. Gluten is a protein found in wheat, rye, and barley. Learn more
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D): It can lead to non-stop diarrhea in attacks (days of flare-ups and days of remissions). However, it may lead to chronic non-stop diarrhea if undiagnosed or untreated. Learn more about IBS.
- Chronic use of certain Medications: Many medications such as Metformin (for Diabetes), Some antihypertensive medications (ACE inhibitors), gastritis & peptic ulcer medications, some antibiotics, some anti-depressants, Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine, and chemotherapy. See the full list HERE.
- Removal of your gallbladder: cholecystectomy can result in diarrhea. Diarrhea can resolve in a few weeks but may last for months.
- Endocrinal diseases: such as hyperthyroidism and Diabetes mellitus.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative Colitis). Learn More.
When to see a doctor?
Generally speaking, you should be medically evaluated for any severe non-stop diarrhea lasting more than two days.
See a doctor if:
- Prolonged non-stop diarrhea (for days or months).
- Passage of blood or blackish stool.
- High-grade fever or low-grade fever that lasts for several days.
- Severe intolerable abdominal pain.
- Persistent vomiting.
- Having chronic diseases such as Diabetes or kidney disease.
- Pus-filled stool.
- Signs of dehydration include extreme thirst, dizziness, rapid heartbeats, or confusion.
- Non-stop diarrhea in aged extremities (elderly or babies).
What are the best remedies for non-stop diarrhea?
The most common cause of acute non-stop diarrhea is viral gastroenteritis (stomach flu). The condition is usually self-limiting within a few days.
No specific treatment for viral gastroenteritis. Only supportive and symptomatic treatments are applied to prevent complications.
Don’t try to self-medicate if you have prolonged or severe diarrhea (high fever, severe vomiting, signs of dehydration).
General remedies that help with acute viral diarrhea:
- Stay hydrated: by drinking lots of water and fluids.
- BRAT Diet: The BRAT (bananas, rice, apple sauce, and Toast) diet is an easily digestible food that improves diarrhea.
- Rest is important to avoid dizziness and complications.
- Some over-the-counter antidiarrheals can be used with caution. But you should better consult your doctor before using them. Immodium and Pepto Bismol are the two most widely used anti-diarrheal.
- Over-the-counter antispasmodics and antiemetics may also help in acute cases.
- A pediatrician should evaluate diarrhea in babies. Babies are more prone to dehydration and may need vigorous rehydration with specific electrolyte solutions (Oral Rehydration Solution or ORS).
- Cause-specific treatments for your diarrhea are needed when the diarrhea is severe or prolonged. Your doctor may order some investigations to diagnose the cause of your prolonged non-stop diarrhea.
MORE:
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.