8 Common Causes of Mushy Stool & Gas.
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
Mushy (loose) stool and gas occur with the various condition. Acute attacks of mushy stool and gas are often due to dietary changes or infection. Chronic mushy stool and gas can be due to irritable bowel syndrome, food intolerance, celiac disease, etc.
Common causes of acute mushy stool and gas:
- Infection (acute gastroenteritis) or food poisoning.
- Recent use of specific medication.
- An attack of food intolerance.
Common causes of chronic or recurrent mushy stool and gas:
- Food intolerances (such as lactose intolerance) and food allergies.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Celiac disease.
- Bile acid diarrhea.
- Gallbladder removal.
- Chronic pancreatitis.
- Others (less common): colorectal cancer, hyperactive thyroid gland, neuroendocrine tumors, and others.
When to see a doctor for a mushy stool and gas:
Here are some notes on the most common causes of mushy stool and gas:
1. Lactose intolerance.
Lactose is a type of sugar mainly present in milk and other dairy products.
Lactose intolerance is the most common form of food intolerance. Studies show that around 25% of the white race has lactose intolerance (reference).
Shockingly, lactose intolerance may affect up to 90% of other races, such as blacks, Native Americans, and Asian Americans (reference).
If you are a regular consumer of milk or dairy products, lactose intolerance can cause mushy stool and gas.
What causes lactose intolerance?
The lactose sugar needs an enzyme called (lactase) to be digested and absorbed. Lactose intolerance occurs when your small intestine cannot produce enough (lactase) (reference).
The lactase enzyme deficiency can be:
- Primary lactase deficiency: is a hereditary disease leading to gradual loss of lactase enzyme function (most common cause).
- Secondary lactase deficiency: due to injury to the intestinal mucosa as with gastroenteritis, celiac disease, IBD, chemotherapy, or antibiotic use.
Symptoms suggestive of lactose intolerance:
- Diarrhea or mushy stool after eating ice cream and other dairy products.
- Stomach pain.
- Bloating and distension.
- Passing too much gas (flatulence).
- Nausea after eating dairy products.
- Fullness and early satiety.
- Vomiting can occur in severe cases.
- Less commonly: Headache, muscle aches, joint pain, mouth ulcers, and impaired concentration (reference).
Lactose intolerance is a widespread condition. So, consider consulting your doctor if you consistently get so much gas all the time.
Also, you can run a small experiment by eliminating dairy for a week and notice the changes in gas amounts. Then, tell your doctor or nutritionist if cutting lactose improves your condition.
More: What happens if you ignore lactose intolerance?
3. Other forms of food intolerance and allergy.
We discussed lactose intolerance above in a separate section because it is widespread.
Other forms of food intolerance also exist. Commonly, fructose and alochol intolerances.
Moreover, food allergy is another food-related reaction that can cause mushy stool and gas. The definitions and differences are explained in the table below.
| Food intolerance | Food allergy |
| Affects 15-20% of the population | Affects nearly 2-5% of adults |
| Difficulty digesting certain types of food (not immune-mediated allergy). | An immune-mediated reaction to certain foods or food components. |
| Causes “recurrent acute” or “chronic” attacks of diarrhea or mushy stool, gas, and bloating. | Usually causes acute attacks related to the ingestion of offending food. |
| Intestinal symptoms: diarrhea, mushy stool, gas, bloating, distension (looking pregnant), and abdominal pain | Intestinal symptoms are the same |
| No extraintestinal symptoms | Extraintestinal symptoms like rashes, urticaria, swollen lips or face, or severe life-threatening allergic reactions. |
| The severity of your symptoms is proportional to the amount you eat from the offending food. | Even trace amounts of the offending food can produce severe symptoms. |
|
Common offending foods:
|
Common offending foods: (examples)
|
3. Infections of the digestive system and food poisoning.
Infections of the digestive system can be acute or chronic. In both cases, symptoms such as mushy stool, abdominal pain, and gas are also present.
Acute attacks of gastroenteritis are mainly caused by stomach viruses such as norovirus and rotavirus. Other forms of infection also occur such as bacterial, protozoa, and parasitic infection.
Infections that last for more than four weeks can cause chronic diarrhea (or mushy stool) and gas. One of the most common causes of chronic gut infections is recurrent clostridioides difficile.
Infectious causes need an evaluation by your doctor to accurately determine the causative organism.
Symptoms of acute viral gastroenteritis (stomach flu):
- Acute onset diarrhea or mushy stool.
- Gas and bloating.
- Stomach (abdominal) cramps.
- Nausea and maybe vomiting.
- Sometimes, gas and bloating occur.
- Low-grade fever.
- It usually lasts for one to 4 days. But diarrhea may become constant for a week or two.
4. Irritable bowel syndrome.
Irritable bowel syndrome affects too many people worldwide. Approximately 10 to 15% of people have IBS (reference).
Surprisingly, Too many people who match the criteria of IBS don’t seek medical advice. Some studies estimated that 60% of people with IBS symptoms don’t know they have the disease! (reference).
IBS has 4 subtypes according to the predominant symptom. What concerns us today is the diarrhea-predominant IBS. Diarrhea-predominant IBS is one of the most common causes of recurrent diarrhea or mushy stool.
Symptoms (how to suspect IBS-diarrhea):
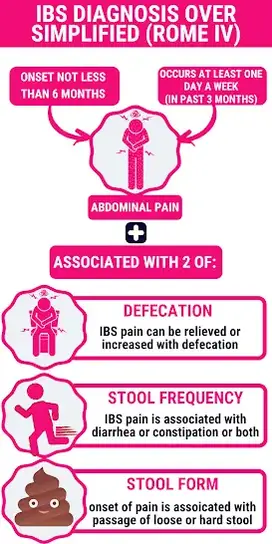
- Abdominal pain: is the fundamental symptom of IBS. IBS sufferers experience abdominal pain at least one day per week for the past 3 months.
- The abdominal pain either improves or worsens after the bowel movement.
- The onset of abdominal pain is associated with diarrhea or loose (mushy) stool (change in stool form).
- Gas and bloating is frequent in people with IBS.
- Intermittent or constant diarrhea.
- Mucus in the stool.
The IBS is usually triggered by:
- Certain foods such as FODMAPs.
- alocholoand caffeine.
- Fatty foods and spicy foods.
- Stress and anxiety.
If you suspect IBS is a cause of constant diarrhea. Learn how is IBS diagnosed in this in-depth article.
5. Medications.
Medications are often overlooked as a cause of diarrhea, loose stool, and gas. Many drugs can result in such digestive problems.
Review your list of medications to exclude medications that can cause mushy stool and gas.
Common medications that commonly cause mushy stool and gas:
- Metformin and gliptins (anti-diabetes medications).
- Antibiotics: particularly penicillins and cephalosporins.
- Laxative overuse.
- Stomach/GERD medications: especially Proton Pump Inhibitors such as Omeprazole (Prilosec), Esomeprazole (Nexium), and Pantoprazole (Protonix).
- Antidepressants such as Citalopram (Celexa) and Escitalopram (Lexapro).
- Chemotherapy.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: such as Ibuprofen (Advil).
- Cholcicine (Colcrys, Mitigare).
- Some anti-hypertensive medications include Enalapril (Vasotec) and Lisinopril (Zestril, Prinivil).
- More than 700 medications can cause diarrhea or loose stool: The complete list is HERE and HERE.
6. Celiac diseases.
Celiac disease is an extreme form of food intolerance. The intolerance to a protein called gluten results in severe intestinal inflammation and interfered with the absorption of various nutrients.
Gluten is present in:
- Wheat-based food (such as bread).
- Rye.
- Barley.
Celiac disease is a relatively common condition. It affects about 1.4% of the people worldwide (reference).
Symptoms:
- The usual age of onset is between 20-30 years of age. But it can occur in older generations up to 70 years.
- Abdominal pain and bloating.
- Diarrhea or mushy stool with gas.
- Celiac disease stool is often loose, yellowish, foul-smelling, and floats on water. Learn more about celiac disease stool changes.
- Diarrhea can also be intermittent or not present. Constipation can also occur.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Weight loss.
- Easy fatigue and iron deficiency anemia.
- Itchy, blistery skin.
- Osteoporosis and osteomalacia (body aches).
Celiac disease is diagnosed by a blood test or biopsy from the small intestine.
Read our in-depth explanation of the stool changes with celiac disease in this article.
Call your doctor if you suspect celiac disease. Learn more.
7. Bile acid diarrhea.
Bile acid diarrhea (BAD) is a common and under-diagnosed condition. BAD can cause recurrent diarrhea or loose stool and gas.
The condition is caused by the inability of your small intestine to handle bile acids. This occurs due to excess bile acids inside your stomach or diseases affecting its absorption.
BAD can cause constant diarrhea and gas for months or years.
The below statistics will explain how common is BAD:
- Approximately 25-50% of patients diagnosed with IBS-diarrhea have BAD (reference).
- It is estimated that about 1% of the population may have BAD.
- About 64% of patients with Functional diarrhea have BAD (reference).
- Up to 35% of people with a condition called “microscopic colitis” have BAD (reference).
Symptoms:
- Constant diarrhea with sudden urges.
- Diarrhea constantly occurs after eating fatty meals.
- Gas and flatulence.
- Bloating and cramps.
- Bile acid diarrhea is differentiated from IBS diarrhea by the characteristic severe urgency that may awaken you at night.
- The urgency can be severe enough to cause soiling accidents.
MORE: Dark Green Poop: 6 Causes Explained.
8. SIBO (small intestinal bacterial overgrowth).
Bloating, gas and mushy stool or diarrhea are the most common symptom of SIBO.
SIBO is an overgrowth of the bacteria living in your intestine, producing extra gas inside your gut.
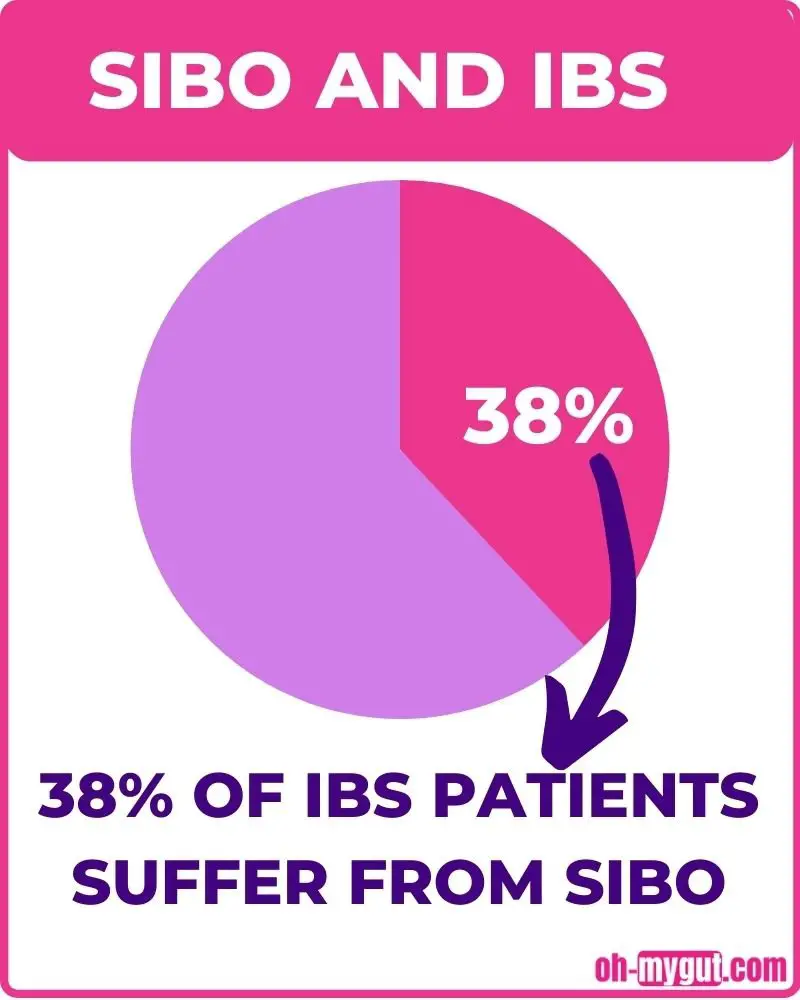
SIBO is more common than you expect. Dr. Binrui Chen and his research team analyzed and reviewed data from 50 studies about SIBO. They found that approximately 38% of IBS patients suffer from SIBO (ref).
SIBO may be the underlying cause of many functional gastrointestinal diseases that presents with bloating.
Risk factors for SIBO may include being a female, old age, and having IBS-Diarrhea.
9. Diabetes.
Damage to the nerves supplying your gut can be a result of long-lasting uncontrolled diabetes. (reference)
This can lead to speeding up (or slowing down) your gut motility. In addition, changes in bowel habits such as getting on and off diarrhea or constipation attacks are common if you have diabetes.
10. Others.
- Chronic pancreatitis.
- Stress and anxiety (acute attacks).
- Crohn’s disease.
- Ulcerative colitis.
- Hyperthyroidism
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Colorectal cancer.
- Lymphoma.
- Addison’s diseases.
- Hormone secreting Gastrointestinal tumors (such as carcinoid syndrome, VIPoma, and gastrinoma).
- And many others.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.