What Are The Signs Of A Perforated Bowel After A Colonoscopy?
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
Following a colonoscopy, the primary indicators of a perforated bowel include sudden intense abdominal pain, tenderness, and localized or widespread abdominal swelling. Other symptoms, such as fever, bloody stool, and low blood pressure, may also be present.
Here is a table summary of signs of perforated bowel after a colonoscopy:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Sudden Severe Abdominal Pain | Acute, severe pain that is steady or increasing, and more extreme than usual gas pain or discomfort. |
| Presence of Blood in Stool | Red or dark blood in stool, especially if the perforation is in the last part of the colon or in the rectum. |
| Rigid, Tender Abdomen | A rigid, tender abdomen with a significant spike of pain on pressure on the affected area. |
| Bloating or Localized Swelling in Your Abdomen | Severe bloating or localized swelling of your abdomen that is not going away for hours. |
| Fever, Chills, or Low Body Temperature | Presence of fever or chills after a colonoscopy, especially if the fever is associated with other signs of a perforated bowel. |
| Severe Nausea or Vomiting | Severe nausea or even vomiting usually occurs with bowel perforation after a colonoscopy. |
| Signs of Low Blood Pressure (Septic Shock) | Symptoms of shock include dizziness, lightheadedness, confusion, restlessness and agitation, cool, pale arms or legs, shortness of breath, rapid breathing, rapid heartbeats, very high or very low body temperature, chills, little or no urine, nausea, lack of appetite. |
| No Symptoms | In rare cases, colon perforation can occur without any symptoms. This is more obvious with people undergoing colonoscopy for diverticulosis, very old age, and people with extremely bad health conditions or very low immunity. |

1- Sudden Severe Abdominal Pain
Experiencing some colicky pain or discomfort post-colonoscopy is normal. However, not every pain you feel indicates bowel perforation (ref).
The abdominal pain resulting from bowel perforation during a colonoscopy is distinct. Let’s delve into the differences.
Bowel perforation due to colonoscopy can be felt during the procedure or shortly after you recover from anesthesia.
Sudden severe abdominal pain is the primary indicator of a perforated bowel post-colonoscopy.
For a comprehensive discussion about the causes of stomach pain after a colonoscopy, Read HERE.
What does the pain from bowel perforation feel like?
The pain is typically acute and more severe (unlike the usual gas pain or discomfort you may feel after a colonoscopy).
The pain is constant, escalating, continuous, and agonizing (not crampy like the usual gas pains post-colonoscopy).
Pain from perforation is usually associated with severe tenderness upon touch. This usually occurs all over the abdomen but is most intense over the perforation site.
When will you start experiencing pain from colon perforation?
The time you start feeling pain due to perforation varies depending on the type of sedation or anesthesia used during the colonoscopy.
During a colonoscopy, your doctor may offer (ref):
No sedation: Very few people choose this, but if you do, you will immediately feel severe pain at the perforation site.Light to moderate sedation: Although sleepy, you know and can obey commands. Also, you will feel significant pain during the colonoscopy procedure. Deep sedation: This is deeper, but you can still respond to painful stimuli, though the response is unpurposeful as your consciousness and memory are impaired with deep sedation. You will soon feel the pain after the sedation wears off. General anesthesia: With general anesthesia, you cannot feel or respond to pain during the colonoscopy. The pain will start after recovery from anesthesia (post-colonoscopy procedure).
People report abdominal pain within the first 24 hours post-colonoscopy. Others may seek medical help after 24 hours.
Interestingly, 25% of patients with bowel perforation post-colonoscopy delay seeking medical help, which can result in complications (ref).
What is the Common Site of Bowel Perforation Pain with Colonoscopy?
The colonoscopy procedure involves only your large intestine and the last few centimeters of the small intestine.
- *Perforation from colonoscopy occurs in the large intestine. A colonoscopy usually doesn’t cause small intestinal, duodenal,
gastric, or esophageal perforation.**
Pain starts in the abdominal area over the perforation site and rapidly spreads over the abdomen.
The most common sites of perforation by colonoscopy are (ref):
Rectum and sigmoid colon {53%}: Starts as lower left abdominal pain and then becomes generalized. Cecum {24%}: starts as lower right abdominal pain and soon becomes generalized all over the abdomen. Ascending colon {9%}: Starts on the right side of your abdomen and spreads.Transverse colon: {9%}: starts at the upper part of your abdomen as abdominal pain under ribs or chest pain.Descending colon {5%}: Starts as left-sided abdominal pain.
MORE: How Far Does Colonoscopy Go?
2- Presence of Blood in Stool
Blood in stool after a colonoscopy can be a normal finding (ref). This usually occurs due to:
Manipulations during colonoscopy can lead to mild trauma inside the colon (without perforation).Certain procedures by the colonoscopist: common procedures causing blood in stool are the removal of a polyp or taking a biopsy. A lesion inside your colon, such as an ulcerated polyp, may bleed after a colonoscopy.
However, perforation can also lead to red or dark blood in the stool, especially if the perforation is in the colon’s or rectum’s last part.
It is not a rule that bleeding occurs with every bowel perforation. So, bleeding per rectum can occur but is not a cardinal sign of perforated bowels.
Unfortunately, the amount of bleeding is irrelevant to the extent of the damage. You can bleed more with polyp removal than from a bowel perforation.
What raises the suspicion:
Bleeding large amounts of blood without a history of procedures during the colonoscopy (such as removing a polyp or taking a biopsy). The onset of bleeding is associated with the sudden severe pain of the perforation ( as I described above). Bleeding that is not going away.
A small transient bleeding per rectum after colonoscopy without significant abdominal pain can occur normally.
3- Rigid, Tender Abdomen
What sets the pain from bowel perforation apart is its association with severe tenderness in your abdomen (ref).
A rigid, tender abdomen with a significant spike of pain on pressure on the affected area is suggestive of bowel perforation.
The tenderness is maximum over the perforation area but expands to the whole abdomen.
Tenderness occurs even with slight movement, walking, or bending of your body.
Normally, you may feel some tenderness over your abdomen after a colonoscopy. But it is milder in severity and unrelated to movement than bowel perforation.
Also, abdominal tenderness due to bowel perforation is usually associated with severe sharp pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
4- Bloating or Localized Swelling (Mass) in Your Abdomen
Again, bloating can occur normally after a colonoscopy (the most common symptom post-colonoscopy).
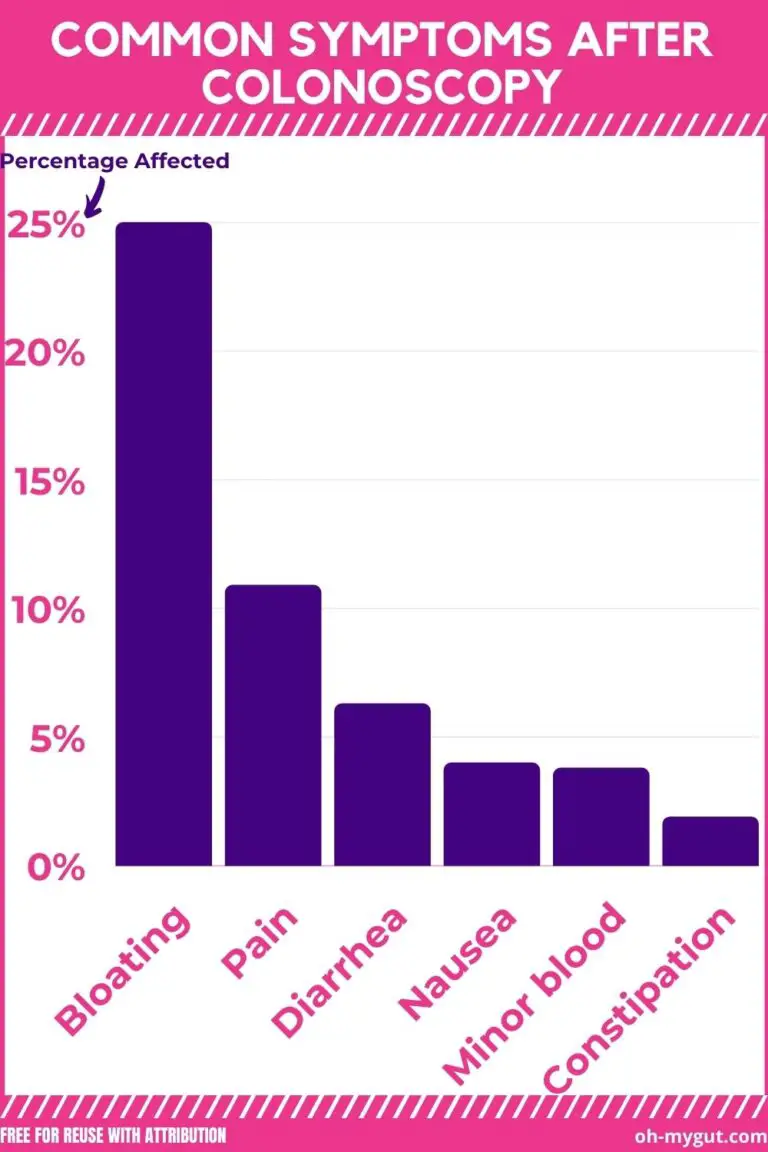
Most people feel bloated after a colonoscopy as your doctor uses air to inflate your colon during the procedure.
Residual air can cause some cramps and bloating sensations as a part of normal post-colonoscopy symptoms.
However, severe bloating or localized swelling of your abdomen that is not going away for hours can occur with bowel perforation (ref).
The bloating is usually associated with severe sharp abdominal pain, abdominal tenderness, nausea, or vomiting.
Bloating without other acute severe symptoms of bowel perforation doesn’t suggest bowel perforation. You don’t have to worry; bloating alone is not a sign of bowel perforation.
5- Fever, Chills, or Low Body Temperature
As a result of bowel perforation, feces, and waste products escape outside the colon. These products can cause inflammation of the lining tissue layer of the abdomen (called the peritoneum).
Not only this, but these septic products can also reach the blood circulation and cause infection and sepsis.
This contamination of the inner tissues and blood with contents from the perforated colon trigger inflammation with chills and fever.
So, fever or chills after a colonoscopy is a warning sign of intestinal perforation, especially if the fever is associated with other signs of a perforated bowel.
However, some patients may experience fever after a colonoscopy for reasons other than perforation, such as:
Few bacteria may leak into the blood without colon perforation or polypectomy (Transient bacteremia).Transient bacteremia after removal of a colon polyp (Polypectomy).Some anesthetic medications (especially with general anesthesia).
Also, hypothermia may occur in some cases where the perforation is associated with severe sepsis (especially if left undiagnosed) (ref.
MORE: General Ill Feeling After Colonoscopy
6- Severe Nausea or Vomiting
Severe nausea or even vomiting usually occurs with bowel perforation after a colonoscopy.
This is because of the severe pain or the leakage of colon contents into the peritoneum, causing inflammation (peritonitis).
Mild nausea or vomiting can normally occur after the colonoscopy due to the following:
- *Effects of the pre-colonoscopy
preparations.Severe gas distension. As a result of sedation or anesthetic medication.**
If nausea and vomiting are associated with severe pain and tenderness, you should seek medical help.
7- Signs of Low Blood Pressure (Septic Shock)
Leakage of stomach contents into the peritoneum and blood may cause a severe form of infection called septic shock.
As a result, bacteria and toxins inside the blood circulation will cause the blood circulation to collapse and cause low blood pressure.
Symptoms of Shock (Low Blood Pressure) Include:
Dizziness, lightheadedness, confusion, or even coma.Restlessness and agitation.Cool, pale arms or legs.Shortness of breath, rapid breathing.Rapid heartbeats (palpitations).Very high or very low body temperature.Chills.Little or no urine.Nausea, lack of appetite.
Learn more about septic shock.
8- No Symptoms!
In rare cases, colon perforation can occur without any symptoms; this is more obvious with (ref):
People are undergoing colonoscopy for diverticulosis. Very old age.People with extremely bad health conditions or very low immunity, as with chemotherapy patients. Tiny perforations can heal spontaneously.
How Can Your Doctor Detect a Perforated Bowel After a Colonoscopy?
If you suspect any signs of bowel perforation after a colonoscopy, you should immediately go to the emergency room.
Here’s what to expect from your doctor or gastroenterologist:
Your doctor will take a detailed history of the post-colonoscopy condition and the symptoms you feel. Perform a detailed abdominal examination, check your vital signs, and they may perform a rectal examination. Your doctor may order lab tests such as a complete blood picture, renal function test, urine sample, C reactive Protein…A plain X-ray in the erect position on your abdomen can diagnose colon perforation. Also, abdominal Ultrasonography, CT, or MRI can be done to confirm the condition. Your doctor may prepare you for surgery, another colonoscopy, or admit you for treatment and observation at the hospital.
FAQs
Q: How common is bowel perforation after a colonoscopy?
A: Bowel perforation after a colonoscopy is a rare but serious complication. It occurs in less than 1% of all colonoscopies.
Q: What should I do if I suspect a bowel perforation after a colonoscopy?
A: If you suspect a bowel perforation after a colonoscopy, you should seek immediate medical attention. This is a serious condition that requires urgent treatment.
Q: Can a bowel perforation heal on its own?
A: In some cases, a small perforation may heal independently. However, larger perforations often require surgery to repair.
Q: What are the long-term effects of bowel perforation?
A: If left untreated, bowel perforation can lead to serious complications, including infection, abscess formation, and sepsis. With prompt treatment, most people recover fully.
Q: Can bowel perforation be prevented?
A: While preventing bowel perforation is impossible, the risk can be minimized by following your doctor’s instructions before and after the colonoscopy. This includes properly preparing for the procedure and reporting any unusual symptoms immediately after the procedure.
Q: How is bowel perforation treated?
A: Treatment for bowel perforation usually involves surgery to repair the hole in the bowel. In some cases, antibiotics may also be given to treat or prevent infection.
Q: Can I sue if I get a perforated bowel from a colonoscopy?
A: If you believe that your bowel perforation was due to medical negligence, you may be able to file a lawsuit. However, it’s important to note that bowel perforation is a known risk of colonoscopy, even when performed correctly. You should consult with a legal professional to discuss your options.
Q: What is the recovery time after a bowel perforation?
A: The recovery time after a bowel perforation can vary depending on the severity of the perforation and the individual’s overall health. It can range from a few weeks to several months.
Q: Can I eat normally after a bowel perforation?
A: After a bowel perforation, your doctor will likely recommend a specific diet to help your bowel heal. This may include a liquid diet, gradually introducing solid foods as your bowel heals. Always follow your doctor’s dietary recommendations.
Q: Can a bowel perforation cause long-term damage?
A: If bowel perforation is not treated promptly, it can lead to serious complications such as peritonitis (inflammation of the lining of the abdomen), abscesses, and sepsis. These complications can cause long-term damage and may be life-threatening. However, with prompt treatment, most people recover fully from bowel perforation.
Q: Are there any risk factors for bowel perforation during a colonoscopy?
A: Certain factors can increase the risk of bowel perforation during a colonoscopy. These include advanced age, previous abdominal surgery, certain medical conditions such as diverticulosis or inflammatory bowel disease, and large polyps or tumors in the colon.
Q: Can bowel perforation occur days after a colonoscopy?
A: While most cases of bowel perforation occur during or immediately after a colonoscopy, it is possible for symptoms to appear a few days later. If you experience severe abdominal pain, fever, chills, or other symptoms of bowel perforation, seek medical attention immediately.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.

Related Posts:
- Passing Clear Liquid From the Bowel: 7 causes,…
- 8 Warning Signs of a Dying Liver (Hepatologist Explains).
- Pancreas Problems: 5 Main Conditions, Symptoms, & Signs
- Can I Eat a Burger After a Colonoscopy? And When?
- Rice After Colonoscopy: What Type Can You Eat?
- Is Bone Broth Okay Before Colonoscopy? GI Doctor Explains.