How Far Does Colonoscopy Go?
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
1. How far does a colonoscopy go?
From its name, the colonoscope goes as far as the entire colon. Also, it can pass through the last part of your small intestine (called the terminal ileum).
Understanding the colon and its length.
Your colon is not a straight vertical structure. Instead, it follows a semi-circular course around your abdomen ending in the rectum and the anal canal.
Your colon is about 120-150 Cm (about 4-5 feet). It starts in your abdomen’s lower right part quadrant with the caecum.
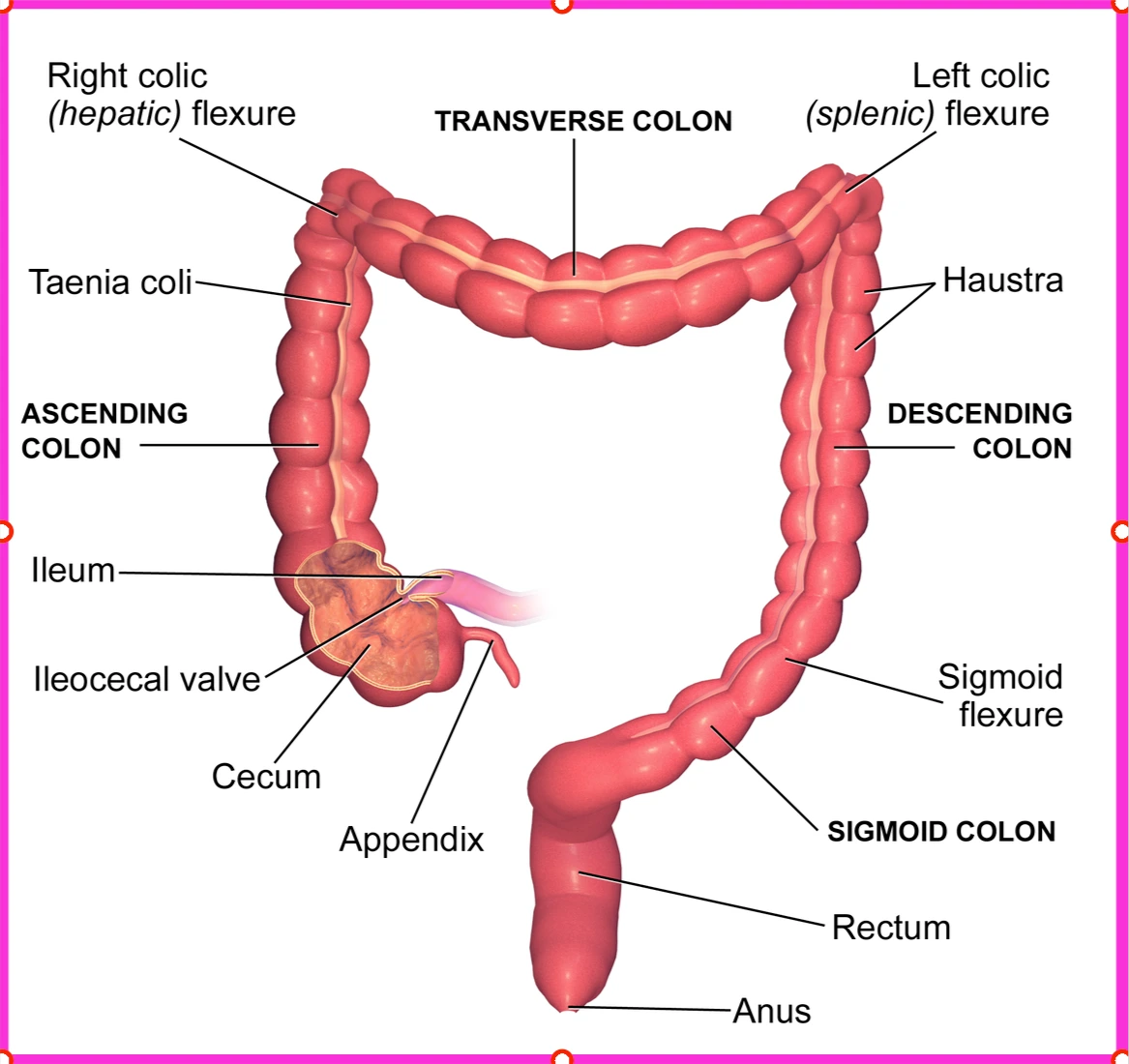
The caecum is a continuation of the last part of the small intestine (called the terminal ileum. The caecum then continues upward as the right ascending colon.
Then, the colon bends to the right to form the horizontal (transverse colon). Finally, near the spleen, the colon goes down again on the left side of your abdomen as the (left descending colon).
Before the rectum, the colon forms an S-shaped segment called the sigmoid colon, which connects the descending colon to the rectum and anal canal.
The following table shows the average lengths of different parts of the colon:
Colon Part | Average length (cm) |
| The caecum | 6-9 |
| Ascending colon | 20-25 |
| Transverse colon | 40-45 |
| Descending colon | 10-15 |
| Sigmoid colon | 35-40 |
| The rectum | 12 |
| The anal canal | 3 |
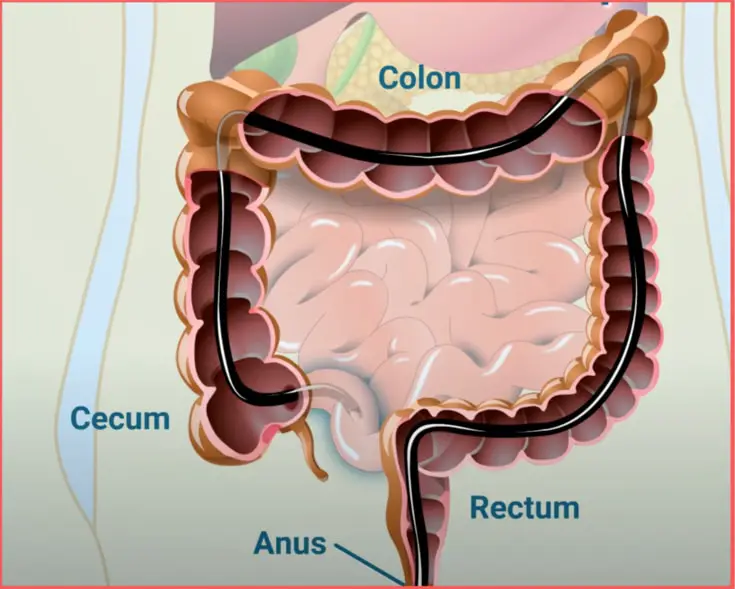
During a colonoscopy, your doctor introduces the colonoscopy through the anal canal and the rectum. Then, the colonoscope slowly advances through the sigmoid, descending, transverse, descending colon to reach the caecum.
The colonoscope often passes through an opening at the caecum as far as the terminal ileum (the last portion of the small intestine).
The terminal ileum is your colonoscope’s farthest point (see the illustration below).
How can the colonoscope go so far?
The colonoscope is a long flexible tube-like device reaching about 170-180 cm. Sometimes, the entire length of the colonoscope goes inside your bowels.
The front tip of the colonoscopy is highly flexible and can be controlled in any direction.
The colonoscopy is capable of going as far as the terminal ilium, aided by:
- Its flexible nature makes loops and takes the shape of your colon.
- It uses air (or Co2) to inflate your colon so it can pass easily.
- The tip of the colonoscopy (last 10 cm) is often very flexible and can be directed to any angle.
- Your doctor may use lubricant on the surface of the colonoscopy to help its passage through the colon.
Can a colonoscopy cause bowel perforation?
The prevalence of bowel perforation during a colonoscopy passage is about 1:1000 to 1:1400.
It is a rare but dangerous complication that can occur due to the passage of the colonoscopy or intervention, such as taking a biopsy or removing a polyp.
The most common site of colonoscopy-related bowel perforation is the rectum and sigmoid colon. The sigmoid colon.
The table below illustrates the perforation frequency according to the part of the colon (reference).
| Colon Part | How common (% of all perforation events) |
| Rectum and sigmoid colon | 53% |
| Caecum | 24% |
| Ascending colon | 9% |
| Transverse colon | 9% |
| Descending colon | 5% |
Symptoms of a perforated bowel after colonoscopy:
- Sudden onset of severe intolerable abdominal pain during or just after the colonoscopy.
- Severe tenderness over the abdomen.
- Blood in the stool (it usually occurs without perforation). Painless bleeding of small amounts of blood is not a cause of concern after a colonoscopy.
- Severe bloating or distension.
- A sense of localized mass after colonoscopy.
- Fever and chills (often start hours after colonoscopy).
- Severe anorexia, nausea, and vomiting.
- Untreated bowel perforation may result in severe bacterial infection and low blood pressure (septic shock).
Should you be worried about a colonoscopy?
No procedure without risks. Compared to surgery, colonoscopy is a relatively safe procedure. In addition, the incidence of complications from colonoscopy is very low.
Don’t overthink the procedure; go for it if your doctor recommends it.
Colonoscopy is very helpful in detecting and preventing serious diseases such as colorectal cancers, inflammatory bowel disease, etc.
So, go for it once recommended by your doctor. Discuss any questions or concerns about the colonoscopy with your gastroenterologist or nurse.
Learn More:
The causes of pain after colonoscopy polyp removal.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.