How Long Does it Take to Get Sick from Food Poisoning? Doctor Explains.
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
The period between eating the offending food and the appearance of symptoms varies according to the cause. On average, It takes about a few hours to 3 days after eating the offending foods to get sick.
However, it may be as short as 30 minutes as with staphylococcal food poisoning. Also, you may take up to 50 days (as with hepatitis A food poisoning).
How long does it take to get sick from food poisoning (according to each organism)?
The period between eating the offending food and getting sick is called the incubation period.
The list below shows the incubation periods of each type of food poisoning from the shortest to the longest:
- The shortest period to get sick is by Clostridium Perfringens bacteria. You take only 8-16 hours to get sick after the infection.
- Some Organisms may take up to one month to cause symptoms. For example, Cryptosporidium protozoa take up to 28 days to make you sick after ingesting it.
The table below illustrates the time needed to get sick from food poisoning according to different organisms (reference).
| Food Poisoning Type | How long does it take to get sick |
| 0. Staphylococcus (the disease is caused by its toxins, not the bacteria). | Thirty minutes to 8 hours. |
| 1. Clostridium Perfringens | 8 – 16 hours |
| 2. Rotavirus, adenovirus, Astroviurs, and Sapovirus | Ten hours to 3 days. |
| 3. Listeria monocytogenes | One day. |
| 4. Norovirus | 1-2 days. |
| 5. E. coli (enterotoxigenic), non-typhoidal salmonella, Shigella (bacillary dysentery), Campylobacter bacteria | 1-3 days. |
| 6. E. coli (Enterohemorrhagic). | 1-8 days. |
| 7. Cyclospora | 1-11 days. |
| 8. Yersinia | 4-6 days. |
| 9. Giardia lamblia | 7-14 days. |
| 10. Entamoeba histolytica | 7-21 days. |
| 11. Cryptosporidium Pavum | 2-28 days. |
What are the most common causes of food poisoning and their incubation periods?
Foodborne illness (AKA food poisoning) is caused by eating foods contaminated with infectious microorganisms or toxins.
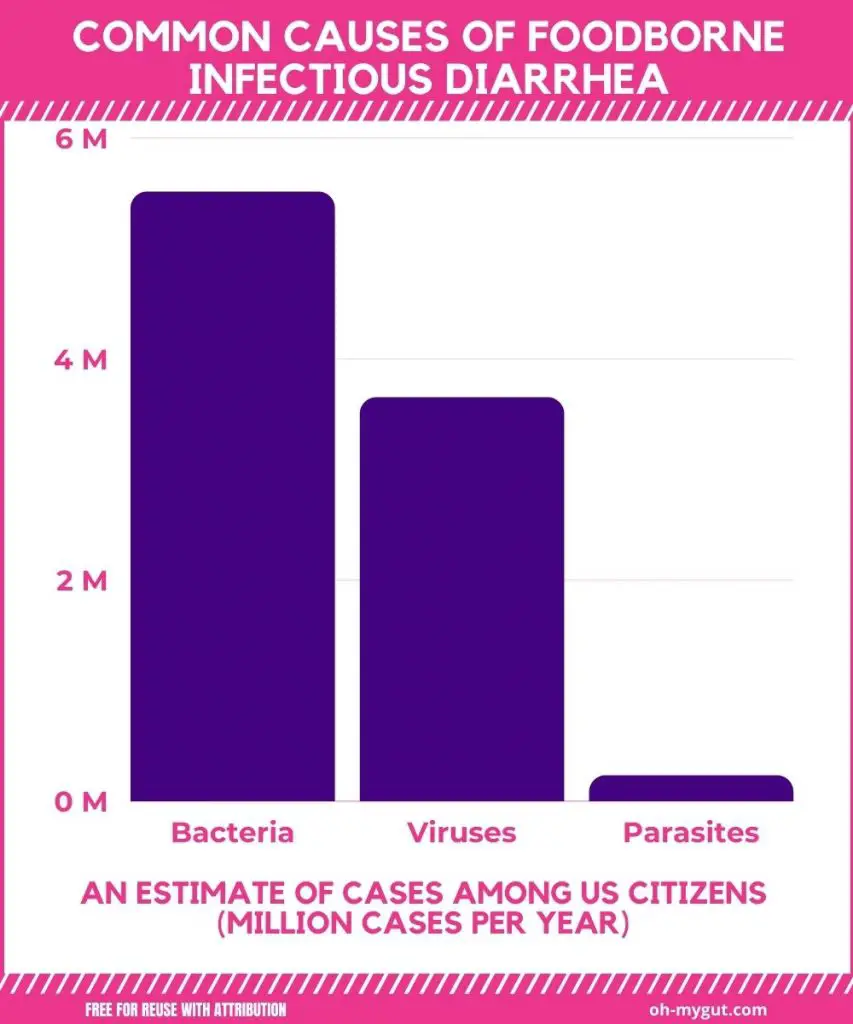
The most common causes of food poisoning in the USA are (reference):
- Viruses (commonest): Affecting about 5.5 million cases per year.
- Bacteria: affecting around 3.6 million per year.
- Parasites: affecting about 233 Thousand per year.
The top 5 most common causes of food poisoning are (reference).
- Norovirus food poisoning: it takes 1-2 days to make you sick.
- Salmonella bacteria (the non-typhoidal type): it takes 1-3 days to make you sick.
- Clostridium perfringens bacteria: It takes only 8-16 hours.
- Campylobacter bacteria: it takes 1-3 days to get sick.
- Staphylococcal bacterial toxin food poisoning: you can get sick as fast as 30 minutes. (see the table below for details).
| Food poisoning causes | Estimate of cases/Year (USA) | Incubation Period |
| 1. Norovirus | 5.46 million (only 26% of cases are foodborne) | 1-2 days |
| 2. non-typhoidal Salmonella | 1.03 million (94% foodborne) | 1-3 days |
| 3. Clostridium perfringens | Nine hundred sixty-six thousand (100% foodborne). | 8-16 hours |
| 4. Campylobacter | 845 thousand (80% foodborne) | 1-3 days. |
| 5. Staphylococcus bacterial toxin | 241 thousand (100% foodborne) | 30 minutes-8hours |
How long does it take to get sick from food poisoning (according to the food source)?
The following are examples of the common types of food involved in food poisoning (reference).
| Food poisoning source | Possible organisms (Incubation Period) |
| 1. Raw seafood |
* Norovirus (1-2 days). |
| 2. Raw eggs | * Salmonella (1-3 days) |
| 3. Undercooked meat or poultry. | * Salmonella (1-3 days). * Campylobacter (1-3days). * E. Coli (STEC), (3-4 days). * Clostridium perfringens (8-16 hours). |
| 4. Unpasteurized Milk or juice. | * Salmonella (1-3 days). * Campylobacter (1-3days). * E. Coli (STEC), (3-4 days). * Yersinia enterocolitica (4-6 days). |
| 5. Unpasteurized soft cheeses | * Salmonella (1-3 days) * Campylobacter (1-3 days). * E. Coli (STEC), (3-4 days). *Yersinia enterocolitica. (4-6 days). * Listeria monocytogenes (1 day). |
| 6. Homemade canned goods. | * Clostridium botulinum (12 h-3 days). |
| 7. Raw hot dogs, deli meat | * Listeria monocytogenes. (1 day). |
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.







