Gastric Emptying Study Results (Infographic): Simplified By A Gastroenterologist.
What does a gastric emptying study diagnose?
The gastric emptying study assesses how fast your stomach empties. The emptying study can detect either delayed gastric emptying (gastroparesis) or rapid gastric emptying (gastric dumping).
1- Gastroparesis.
With gastroparesis, your stomach is unable to effectively process the food inside. As a result, food stays longer inside your stomach.
Gastroparesis is caused by (ref):
- Idiopathic: In approximately half of the cases of gastroparesis, doctors cannot detect a specific cause. (ref)
- Diabetes Mellitus: The most recognized cause of gastroparesis.
- Viral infections: Some studies show that gastroparesis can occur due to some viral infections. Common viruses associated with gastroparesis are Norovirus and Rotavirus. (ref)
- Some medications: As antihypertensive medications, Tricyclic antidepressants, Clonidine, GLP-1 agonists (anti-diabetes medication). (ref)
- Post-surgical: Accident or intended injury to the vagus nerve during options can lead to gastroparesis.
- Some neurological diseases: such as Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Brain stem strokes, Brain stem tumors, and Parkinson’s disease.
- Others: such as autoimmune diseases, Scleroderma, and others.
Symptoms of Gastroparesis include:
- Nausea (93%)
- Vomiting (Up to 84%)
- Abdominal pain or discomfort (Up to 90%).
- Early satiety (Up to 86%)
- Fullness after meals, bloating.
- Weight loss in severe cases.
Learn more about gastroparesis.
2- Gastric dumping.
Gastric dumping is defined as RAPID gastric emptying. As a result, sugar rapidly moves from the stomach to the intestine producing symptoms Such as:
- Diarrhea.
- Feeling bloating or too full after eating.
- Abdominal pain or cramps (usually 10 to 30 minutes after eating).
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Flushing, dizziness, lightheadedness.
- Rapid heart rate.
Common causes of dumping syndrome include: (ref)
- Removal of all or a part of your stomach.
- A gastric bypass surgery.
- Esophageal surgery.
Gastric emptying study results explained:
The most simple, cost-effective, and widely available technique is the “Scintigraphic gastric emptying” study. During the study, You typically ingest a small meal containing a radioactive substance. The meal can be:
- Solid (Typically egg white): the most common.
- Liquid: used if dumping syndrome is suspected, or if the patient is too ill to ingest a solid meal.
A specific gamma camera detects the percentage of emptying of the stomach. Typically at one, two, and four hours.
1- Normal values.
Normal values of the gastric emptying study (for the solid meal) are:
- At one hour after the meal: 37-90% of the meal is still inside your stomach.
- At 2 hours: 30-60%. (more than 60% is considered delayed gastric emptying).
- At 4 hours: 0-10%. (More than 10% at 4 hours is considered delayed gastric emptying).
You should note that these numbers are different according to the hospital or center performing the test.
Each center has its reference values and times of measurement. Ask your doctor about the reference values for your specific test.
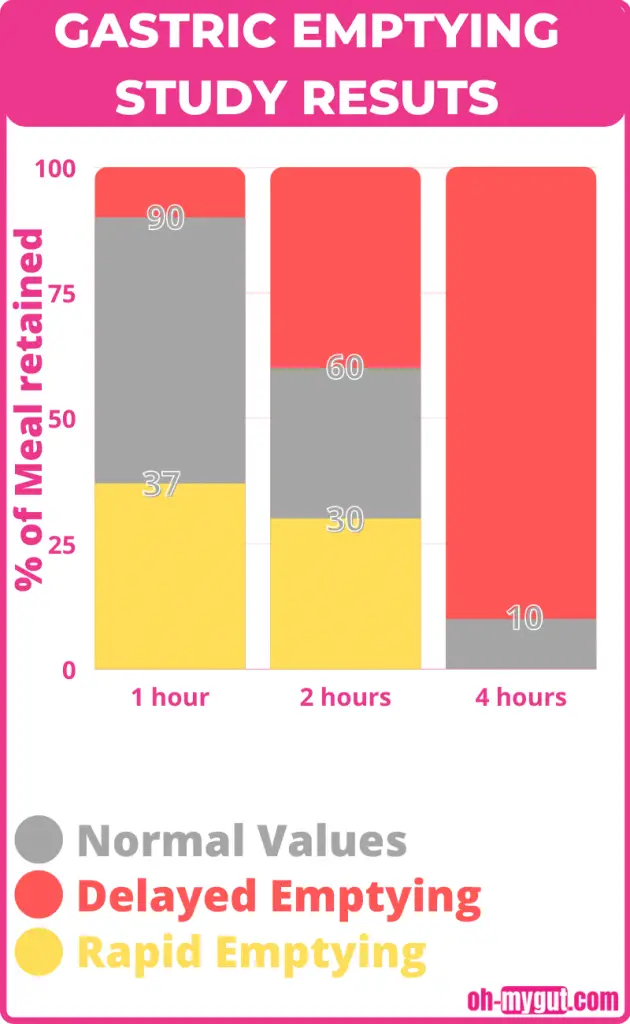
2- Abnormal gastric emptying time (for gastroparesis).
Delayed gastric emptying (gastroparesis) is defined as gastric retention of:
- More than 60% gastric retention at 2 hours.
- More than 10% gastric retention after 4 hours.
Again, note that the above values are specific for the standard low-fat sold meal study.
Further classification of the severity of the gastroparesis (delayed gastric emptying) is obtained at the 4 hours measurement.
According to the percentage of meal retained at 4 hours, delayed gastric emptying is classified into:
- Mild: 10-15% of the meal is still retained.
- Moderate: 15-35%
- Severe: more than 35%.
3- Borderline delayed gastric emptying.
Borderline delayed gastric emptying results are gastric retention values around 60% at 2 hours or 10% at 4 hours. When the results are borderline, your doctor may correlate the borderline result with your symptoms to decide the best management. Also, Your doctor can request other tests or investigations to assess the condition.
Other gastric emptying tests include:
- Wireless motility capsule: learn more
- Breath test: learn more.
4- Abnormal gastric emptying time (for gastric dumping).
We diagnose gastric dumping mainly on a clinical basis. The presence of symptoms and a history of stomach surgery is usually sufficient.
We use gastric emptying results to support the diagnosis.
Less than 30% gastric retention at one hour is highly sensitive and specific for gastric dumping.
FAQs about gastric emptying study results:
1- Can I have gastroparesis with a false-negative gastric emptying study?
False-negative results of the gastric emptying study are highly unlikely. According to the studies, the test has 100% sensitivity at both 2 and 4 hours. A 100% sensitivity rate essentially means a 0% false-negative rate.
2- What does it mean to have the symptoms of gastroparesis with a negative gastric emptying study?
As we explained before, a false negative test for the gastric emptying study is unlikely. If you have symptoms consistent with gastroparesis, it is better to think of alternative diagnoses: (ref)
- Psychiatric diseases.
Vomiting, lost appetite, abdominal pain, and other symptoms of gastroparesis can be due to psychic factors. Stress, depression, anxiety, anorexia Nervosa, and psychogenic vomiting can cause similar symptoms. - Rumination syndrome.
Daily, effortless regurgitation of undigested food soon after eating (without nausea). it is common with psychological illness. It affects both children and adults. - Functional dyspepsia.
Functional dyspepsia is a very common condition. It affects about 10% to 30% of people worldwide. FD is characterized by early satiety, postprandial fullness, and epigastric pain similar to gastroparesis. - Cyclic vomiting syndrome.
Recurrent attracts of intense nausea and vomiting lasting for hours or days. In between the attacks, the person is symptom-free.
3- How long does it take to get results from a gastric emptying study?
The Nuclear medicine specialist will interpret the image as soon as your test ends. He will write a report and deliver it to your doctor.
The time needed to get the gastric emptying results depends on the center or the hospital performing tests. Usually, you can get the results within a day or two. Ask your doctor or Physician assistant about the time it takes to get the results.
Related Posts:
- What Does Lactase Enzyme Do? (Infographic).
- How Is IBS Diagnosed: Over-Simplified (With Infographics)!
- How To Diagnose IBS (Simplified + Quiz), Doctor Explains.
- Bright Yellow Watery Diarrhea: 6 Causes Simplified…
- What Does C. Difficile Poop Look Like?…
- Can Stress Cause Appendicitis? Gastroenterologist Explains.







