Diarrhea After Hiatal Hernia Surgery: Causes & Treatments.
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
Diarrhea after hiatal hernia surgery can be acute due to dietary changes or antibiotic use. Also, it may become chronic due to the development of dumping syndrome.
A. How common is diarrhea after hiatal hernia surgery?
Diarrhea after hiatal hernia surgery is common. For example, 9% of patients may experience diarrhea within the first three months after the surgery. And about 1% may continue to have diarrhea for over three months.
Another study assessed the frequency of diarrhea after anti-reflux or hiatal hernia surgery and found that diarrhea is present in 18-33%.
How long does diarrhea last after hiatal hernia surgery?
However, most cases of diarrhea after the hiatal hernia surgery are temporary and caused by dietary alternations or medications.
The table below illustrates the prevalence of diarrhea after fundoplication surgery for acid reflux (reference).
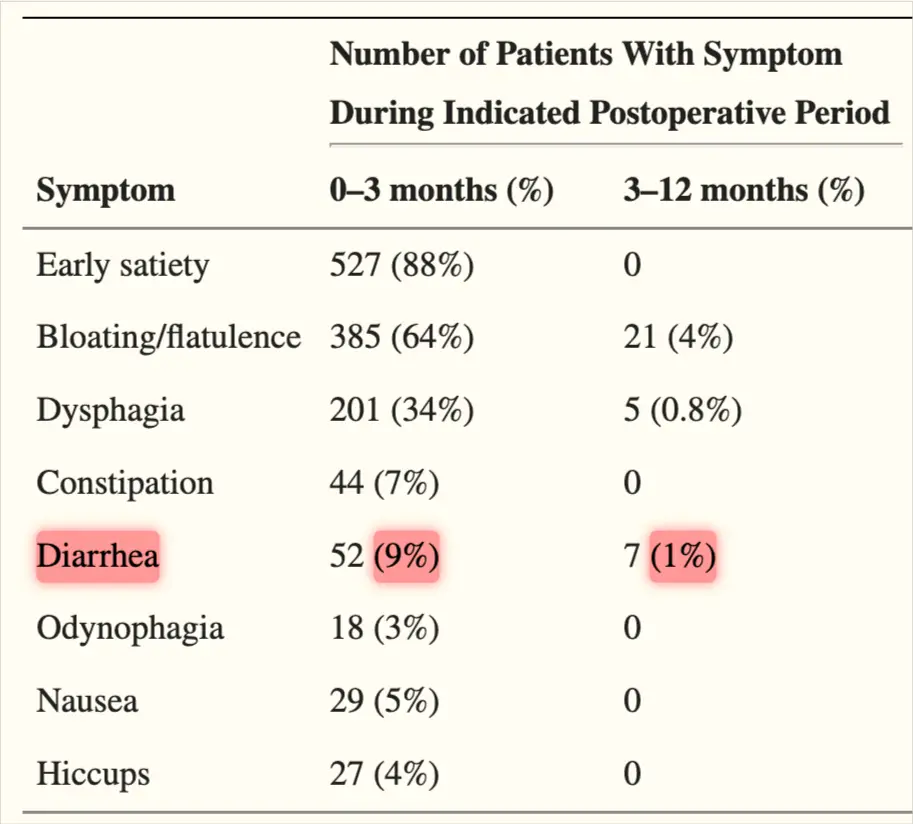
Other common symptoms after hiatal hernia surgery include:
- Early satiety (88%).
- Bloating, gas, or flatulence (in about two-thirds of the patients).
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) in about one-third of the patients.
- Painful swallowing (3%).
- Nausea (5%).
- Hiccups (4%)
B. Causes of diarrhea after hiatal hernia surgery.
Several factors may cause diarrhea after hiatal hernia surgery. The most common causes include dietary changes (Nissen liquid and soft diet), bacterial overgrowth, antibiotic use, prolonged PPI use, and dumping syndrome.
1. Dietary changes.
There are four stages of diet after hiatal hernia surgery:
- Clear liquid diet (often for the first to two days after the operation).
- Full liquid diet (after clear liquid diet, for another day or two).
- A soft diet (for the next 4-8 weeks after the operation).
- Lifelong dietary modifications to prevent attacks or recurrence of reflux symptoms after the hiatal hernia operation.
These specific diet regimens are described for at least one month after the operation. Nissen’s soft diet is often fundamentally different from the usual diet for most people.
As a result, your gut may find difficulty digesting these special types of diet.
Common dietary changes that may lead to diarrhea after hiatal hernia surgery:
- Excess fruit juice especially fruits with high fructose, such as apple juice.
- Excess lactose in milk and dairy products.
- Excess fructans in leafy vegetables and cereals.
Eating lactose, fructose, or fructans in moderation often doesn’t lead to diarrhea in most people. However, in the post-surgery stage, your specific diet often contains excess amounts of these contents leading to diarrhea.
Work with a doctor or dietitian to determine the exact diet causing diarrhea and modify your diet plan based on your symptoms.
2. Infection (gastroenteritis) or Bacterial overgrowth.
Bacterial Overgrowth:
Bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine can occur due to a variety of causes such as (reference):
- Profound dietary changes.
- Injury to the vagus nerve during surgery.
- Prolonged use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) such as omeprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole, and dexalansoprazole.
These factors may alter the normal (beneficial) bacteria inside your small intestine leading to diarrhea after surgery. In addition, the condition is often associated with gas, bloating, and recurrent abdominal cramps.
Infection (acute gastroenteritis):
Infection (acute gastroenteritis) is often caused by viruses (such as norovirus or rotavirus).
It is a common gastrointestinal disorder that may cause diarrhea after hiatal hernia surgery.
Its symptoms include acute onset watery diarrhea, lower abdominal cramps, fatigue, low-grade fever, nausea, or vomiting. It is often self-limiting within a few days. Learn More.
3. Drug-induced diarrhea (mainly antibiotics).
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics after the hiatal hernia surgery to prevent infection at the surgical site. However, many people may get diarrhea (mild or severe) from taking antibiotics.
The diarrhea is often in the first few days after starting the antibiotics.
Common antibiotics that cause diarrhea include:
- Macrolides such as clarithromycin and azithromycin.
- Penecillins such as amoxicillin
- Cephalosporin antibiotics such as Ceftriaxone.
- Fluoroquinilones such as ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin.
4. Exacerbation of Irritable bowel syndrome.
Acid reflux (GERD) and IBS are closely related. For example, studies found that:
- 33.9% of GERD patients had IBS.
- And 63.6% of IBS patients had GERD.
So, chronic or recurrent diarrhea may be due to undiagnosed IBS. The main hallmark of this disease is the presence of diarrhea BEFORE the anti-reflux surgery.
Irritable bowel syndrome is often triggered by diets such as Nissen liquid and soft diet, exacerbating diarrhea after the surgery.
Symptoms of IBS include:
- Recurrent abdominal pain (generalized) has occurred at least once per week for the last three months.
- Stool changes (soft or hard stools at the onset of the pain).
- Diarrhea and/or constipation attacks.
- Bloating and recurrent flatulence.
- The pain often improves after passing flatus or stool.
5. Dumping syndrome.
Dumping syndrome is defined as rapid stomach emptying after eating. As a result, your digestive system (stomach and small intestine) will not have enough time to process food properly.
Dumping syndrome can occur after esophageal surgery, including hiatal hernia surgeries such as Nissen fundoplication. However, Severe dumping syndrome is rare.
Symptoms of dumping syndrome after the hiatal hernia surgery:
- Diarrhea.
- Feeling bloating or too full after eating.
- Abdominal pain or cramps (usually 10 to 30 minutes after eating).
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Flushing, dizziness, lightheadedness.
- Rapid heart rate.
D. Treatment tips for diarrhea after hiatal hernia surgery.
- Identifying the cause is the most important step in treatment.
- Dietary modifications to eating less fructose, lactose, and fructans (especially in people with IBS).
- Probiotics may help with bacterial overgrowth, IBS, and antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
- OTC antidiarrheals, such as loperamide, if the condition is severe.
- Stay hydrated (drink plenty of fluids).
- Avoid medications that may cause diarrhea. Discuss the issue with your doctor. Don’t stop essential medications such as antibiotics and PPIs without medical permission.
- Keep a food diary to help you figure out the offending foods.
E. when to see a doctor.
Seek medical assistance if diarrhea after hiatal hernia surgery is:
- Severe (5 or more attacks per day).
- Mild but prolonged for severe days or weeks.
- Associated with severe abdominal pain.
- Associated with bloody stool.
- Associated with vomiting.
- Associated with dehydration (dizziness, lightheadedness, shortness of breath, palpitations, fainting, extreme thirst, or peeing too little urine).
- Associated with fever.
- If you have a medical condition or a weak immune system such as diabetes, kidney disease, etc.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.