What Causes An IBS Flare-up: The Ultimate List (Dr. Farahat)
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
Welcome to the most unpredictable, irrational disease on planet Earth; Irritable bowel syndrome. IBS is probably the most confusing disease.
This is because we cannot expect a definite pattern of symptoms. Also, sometimes we cannot define the cause of an IBS flare-up.
The most common causes of An IBS flare-up are:
- Eating high FODMAP foods and Drinks.
- Fatty and fried foods.
- Large meals (even if it is low in FODMAPS).
- Anxiety, stress.
- Pain, Physical stress, major trauma, and fever.
- Lack of sleep.
- Gut bugs (gastroenteritis).
- Some medications, such as antibiotics.
- Fluctuations in female hormones.
Today I will share all the possible causes of an IBS flare-up as a doctor and an IBS sufferer.
1- Food causes of IBS flare-ups.
A- FODMAP fruits.
FODMAPs are a type of fiber that is proven to trigger your IBS. They are highly fermentable inside your colon, causing IBS flare-ups. Identifying and eliminating these FODMAPs is the best food strategy to prevent IBS flare-ups (reference).
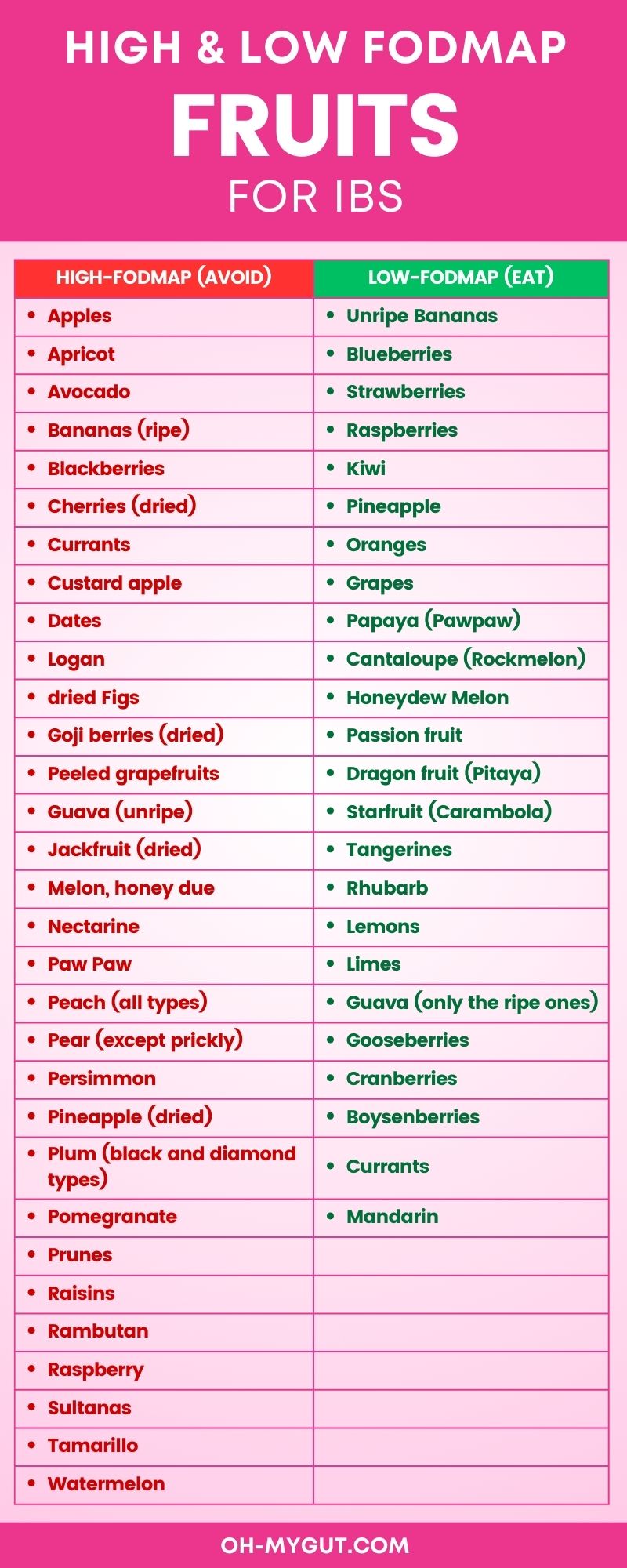
The complete list of high FODMAP fruits:
- Apples
- Apricot
- Avocado
- Bananas (ripe)
- Blackberries
- Cherries (dried)
- Currants
- Custard apple
- Dates
- Logan
- dried Figs
- Goji berries (dried)
- Peeled grapefruits
- Guava (unripe)
- Jackfruit (dried)
- Melon, honey due
- Nectarine
- Paw Paw
- Peach (all types)
- Pear (except prickly)
- Persimmon
- Pineapple (dried)
- Plum (black and diamond types)
- Pomegranate
- Prunes
- Raisins
- Rambutan
- Raspberry
- Sultanas
- Tamarillo
- Watermelon
What are low FODMAP fruits to eat instead:
- Unripe Bananas
- Blueberries
- Strawberries
- Raspberries
- Kiwi
- Pineapple
- Oranges
- Grapes
- Papaya (Pawpaw)
- Cantaloupe (Rockmelon)
- Honeydew Melon
- Passion fruit
- Dragon fruit (Pitaya)
- Starfruit (Carambola)
- Tangerines
- Rhubarb
- Lemons
- Limes
- Guava (only the ripe ones)
- Gooseberries
- Cranberries
- Boysenberries
- Currants
- Mandarin
And always remeber that individual tolerenace may varie and the best way is to keep a food dairy. You can also download the Monash FODMAP app on your phone.
DOWNLOAD THE FREE IBS FOOD GUIDE NOW
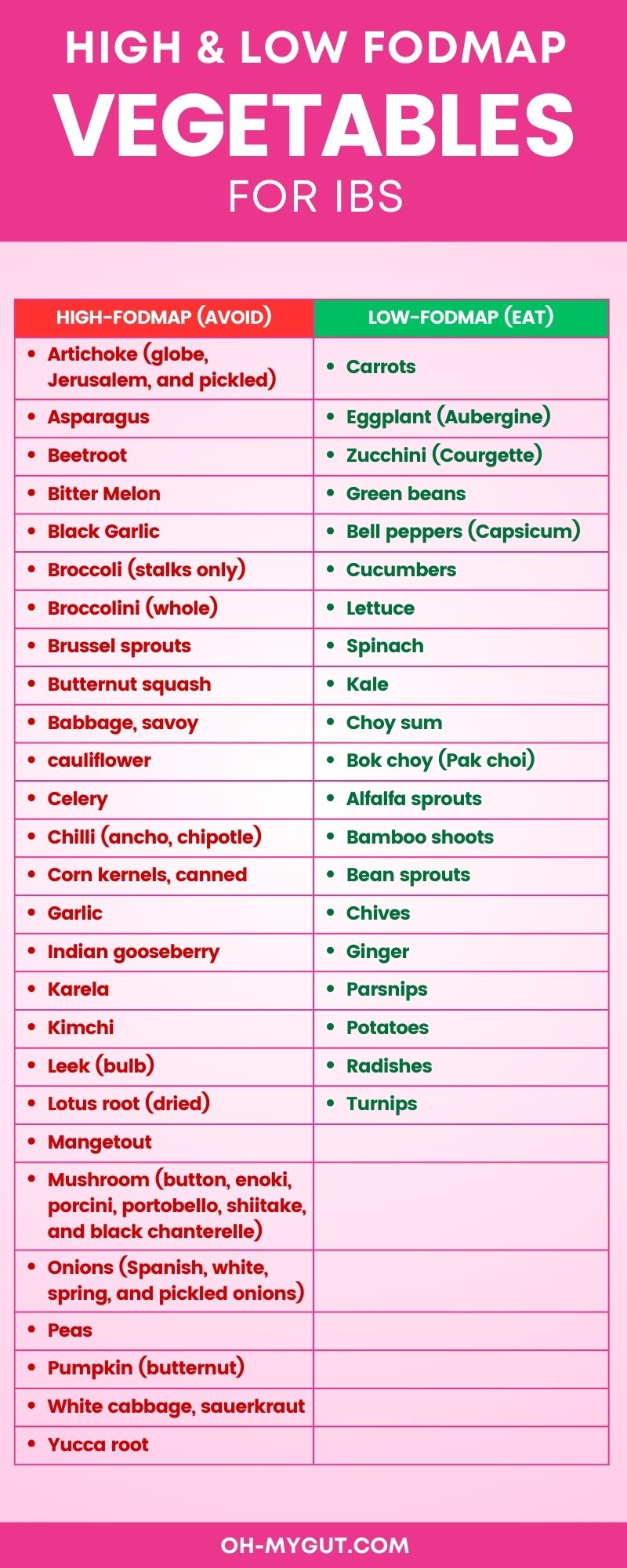
B- FODMAP vegetables.
- Artichoke (globe, Jerusalem, and pickled)
- Asparagus
- Beetroot
- Bitter Melon
- Black Garlic
- Broccoli (stalks only)
- Broccolini (whole)
- Brussel sprouts
- Butternut squash
- Babbage, savoy
- cauliflower
- Celery
- Chilli (ancho, chipotle)
- Corn kernels, canned
- Garlic
- Indian gooseberry
- Karela
- Kimchi
- Leek (bulb)
- Lotus root (dried)
- Mangetout
- Mushroom (button, enoki, porcini, portobello, shiitake, and black chanterelle)
- Onions (Spanish, white, spring, and pickled onions)
- Peas
- Pumpkin (butternut)
- White cabbage, sauerkraut
- Yucca root
Possible low-FODMAP vegetable that you colon may tolerate (trial and error to test your body’s response):
- Carrots
- Eggplant (Aubergine)
- Zucchini (Courgette)
- Green beans
- Bell peppers (Capsicum)
- Cucumbers
- Lettuce
- Spinach
- Kale
- Choy sum
- Bok choy (Pak choi)
- Alfalfa sprouts
- Bamboo shoots
- Bean sprouts
- Chives
- Ginger
- Parsnips
- Potatoes
- Radishes
- Turnips
DOWNLOAD THE FREE IBS FOOD GUIDE NOW
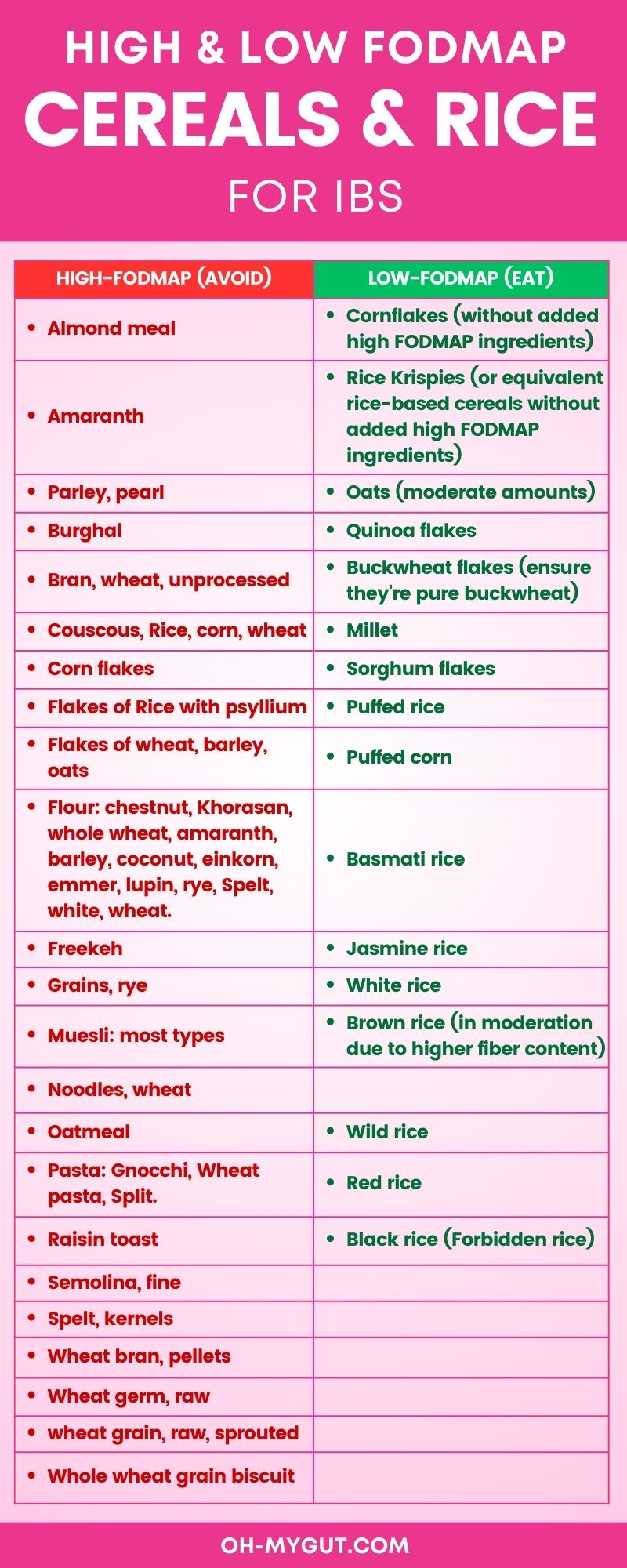
C- FODMAP cereals & Rice.
- Almond meal
- Amaranth
- Parley, pearl
- Burghal
- Bran, wheat, unprocessed
- Couscous, Rice, corn, wheat
- Corn flakes
- Flakes of Rice with psyllium
- Flakes of wheat, barley, oats
- Flour: chestnut, Khorasan, whole wheat, amaranth, barley, coconut, einkorn, emmer, lupin, rye, Spelt, white, wheat.
- Freekeh
- Grains, rye
- Muesli: most types
- Noodles, wheat
- Oatmeal
- Pasta: Gnocchi, Wheat pasta, Split.
- Raisin toast
- Semolina, fine
- Spelt, kernels
- Wheat bran, pellets
- Wheat germ, raw
- wheat grain, raw, sprouted
- Whole wheat grain biscuit
Possible low-FODMAP cereals and rice to eat:
Cereals:
- Cornflakes (without added high FODMAP ingredients)
- Rice Krispies (or equivalent rice-based cereals without added high FODMAP ingredients)
- Oats (in moderate amounts)
- Quinoa flakes
- Buckwheat flakes (ensure they’re pure buckwheat)
- Millet
- Sorghum flakes
- Puffed rice
- Puffed corn
Rice:
- Basmati rice
- Jasmine rice
- White rice
- Brown rice (in moderation due to higher fiber content)
- Arborio rice (commonly used for risotto)
- Wild rice
- Red rice
- Black rice (also known as forbidden rice)
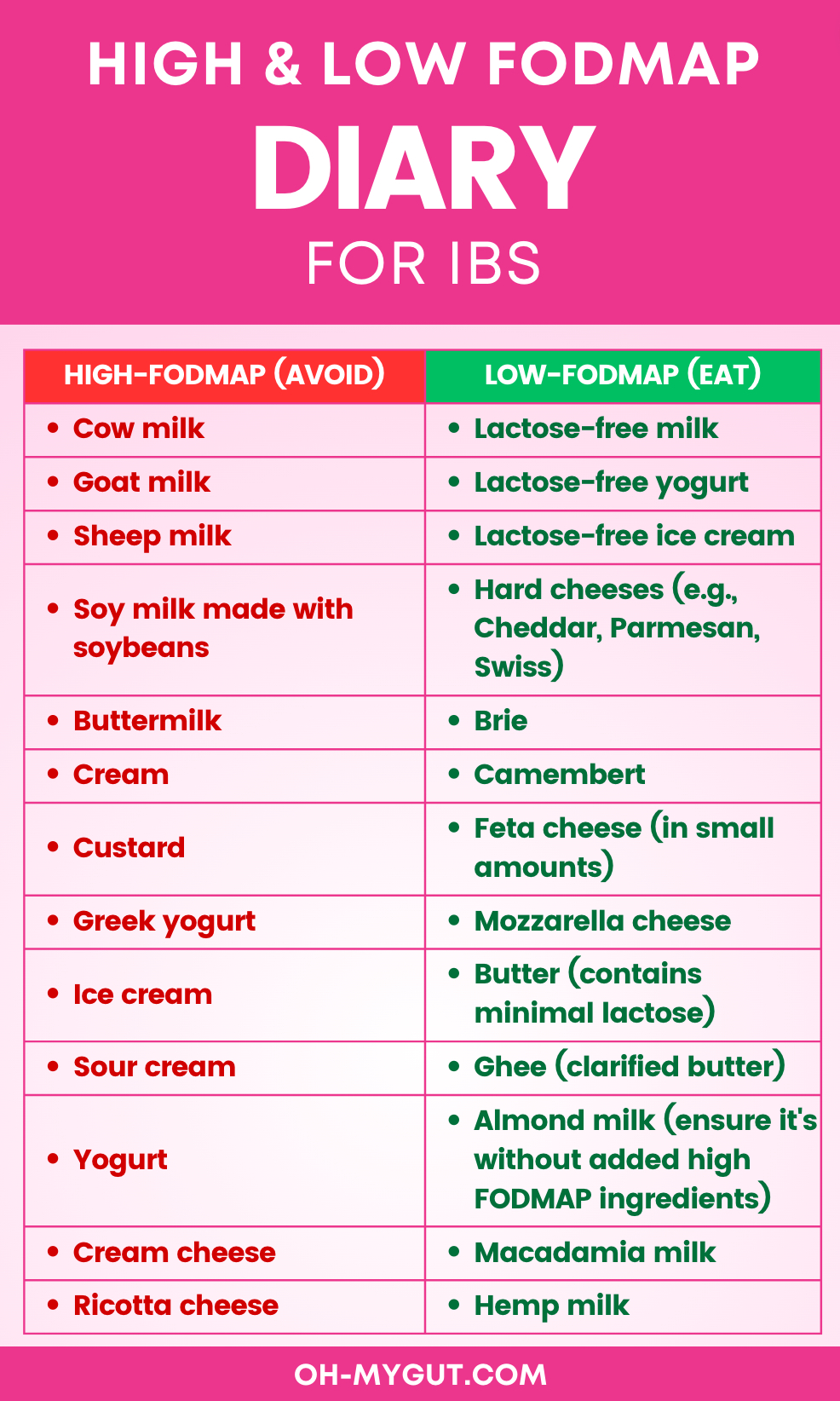
D- Dairy.
- Cow milk
- Goat milk
- Sheep milk
- Soy milk made with soybeans
- Buttermilk
- Cream
- Custard
- Greek yogurt
- Ice cream
- Sour cream
- Yogurt
- Cream cheese
- Ricotta cheese
Here are low-FODMAP dairy options you can consume with IBS
- Lactose-free milk
- Lactose-free yogurt
- Lactose-free ice cream
- Hard cheeses (e.g., Cheddar, Parmesan, Swiss)
- Brie
- Camembert
- Feta cheese (in small amounts)
- Mozzarella cheese
- Butter (contains minimal lactose)
- Ghee (clarified butter)
- Almond milk (ensure it’s without added high FODMAP ingredients)
- Macadamia milk
- Hemp milk
DOWNLOAD THE FREE IBS FOOD GUIDE NOW
F- Alcohols:
- Ciders.
- Cocktails
- Mixers
- Sweet wines
- High fructose corn syrup
- Diet alcohols (contain artificial sweeteners)
- Carbonated alcohols such as Fizzyomixers,0ciders, and sparkling wine.
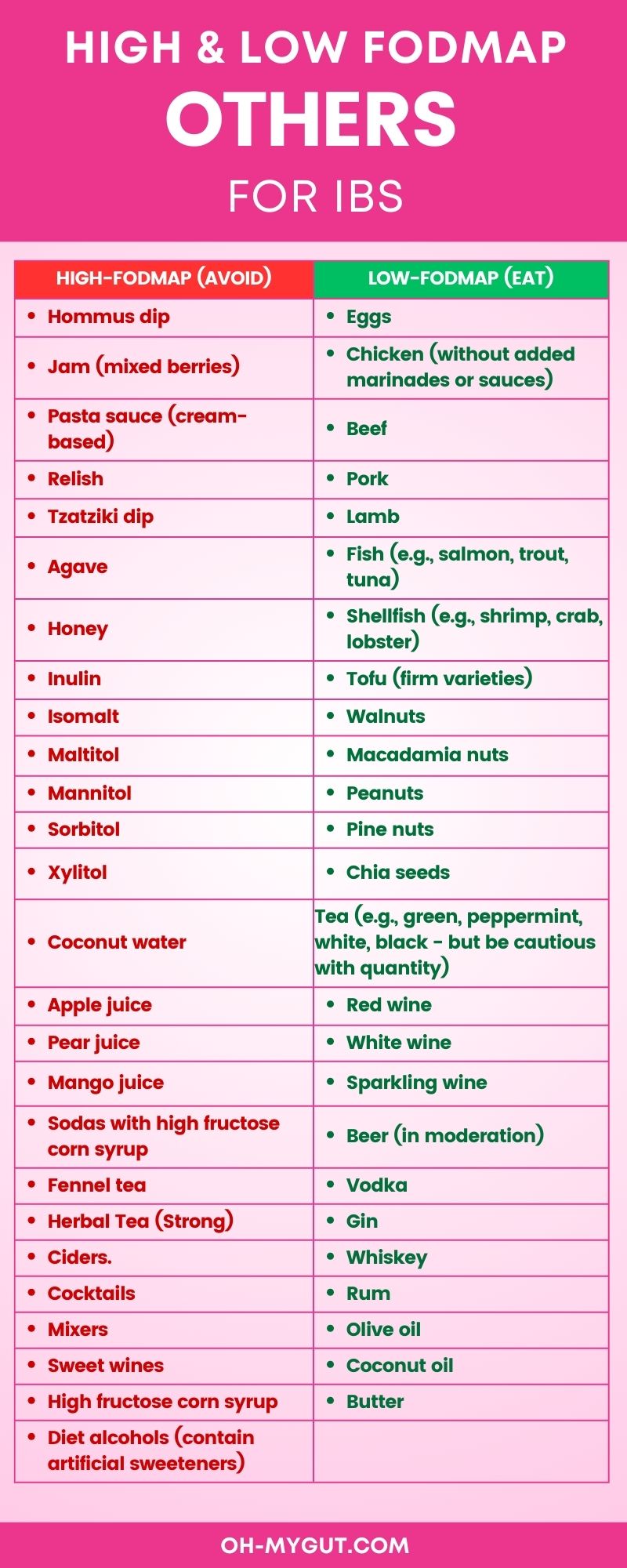
G- Other high FODMAP foods and drinks:
- Hommus dip
- Jam (mixed berries)
- Pasta sauce (cream-based)
- Relish
- Tzatziki dip
- Agave
- Honey
- Inulin
- Isomalt
- Maltitol
- Mannitol
- Sorbitol
- Xylitol
- Coconut water
- Apple juice
- Pear juice
- Mango juice
- Sodas with high fructose corn syrup
- Fennel tea
- Herbal Tea (Strong)
Alternatives that you can consume with IBS:
Proteins:
- Eggs
- Chicken (without added marinades or sauces)
- Beef
- Pork
- Lamb
- Fish (e.g., salmon, trout, tuna)
- Shellfish (e.g., shrimp, crab, lobster)
- Tofu (firm varieties)
Nuts & Seeds:
- Walnuts
- Macadamia nuts
- Peanuts
- Pine nuts
- Chia seeds
- Pumpkin seeds (in small amounts)
- Sunflower seeds (in small amounts)
Beverages:
- Coffee (preferably black or with lactose-free milk)
- Tea (e.g., green, peppermint, white, black – but be cautious with quantity)
- 100% pure cranberry juice (in small amounts)
- 100% pure orange juice (without pulp and in small amounts)
- 100% pure pineapple juice (in small amounts)
Oils & Fats:
- Olive oil
- Coconut oil
- Butter
- Ghee (clarified butter)
SEE our recommended IBS resources and supplements.
DOWNLOAD THE FREE IBS FOOD GUIDE NOW (MOBILE-OPTIMIZED)
G- Fatty or Fried foods.
A survey of 300 patients with IBS found that 40% of the patients with IBS attributed their IBS flare-ups to consuming fatty foods.
So, the consumption of high-fat foods can trigger your IBS symptoms. Examples of High-fat foods to avoid:
- Pizza
- Deep-fried foods
- Creams
- Fatty cuts of beef, pork, or lamb.
- Dark chicken meat and poultry skin
- Lard
- Other fast foods such as burgers, fried chicken … etc
H- Caffeine.
Caffeine and caffeinated drinks are known as triggers for IBS pain and diarrhea. Avoid too much caffeine in your foods and drinks. Also, you can consume deffinated coffee or other decaffinated drinks (provided that they have other high-FODMAP ingredients) safely with IBS.
2- The “amount” of food you eat also matters (large meals can cause Flare-ups).
Eating too much food can trigger your IBS symptoms by:
- Eating too Much “low FODMAP”: From the name, you can expect that “low FODMAP” foods are “No FODMAP.”
So, eating too much “low FODMAPs” will turn the food into a “high FODMAP” food.
To know the exact amount of low FODMAP foods, use the MONASH University FODMAP app (available for both iOS and Android users). - Eating too many different Low-fodmaps will also cause symptoms.
- More colon distension: some studies state that the colon of the IBS patient is more sensitive to distension and gas. And the more food you eat, the more flare-ups you get (reference)
- Increased motility of your colon: eating large meals causes your colon motility to increase, causing painful cramps (reference).
So, It is important to avoid binge eating or large meals. It is time to change your food behavior and live a healthy life.
3- Stress, anxiety, and other psychological conditions.
Your colon has numerous nerve plexuses forming the “second brain.”
From my career as a gastroenterologist, I found that the Digestive system is the most affected by mental health issues and stress.
Many functional gut diseases (not only IBS) are related to anxiety, stress, and psychological dysfunction. For example, GERD, Functional dyspepsia, Functional nausea and vomiting, and Eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa.
This study found that anxiety is far more common among IBS patients than in the general population (44% vs. 8%).
Every time you are subjected to a stressful event or anxiety attack, your IBS may flare up; some examples of IBS triggers:
- Daily stressful events such as exams, work events, public speaking … etc.
- Traumatic events such as the death of a beloved one.
- Depression
- Phobias and health anxiety (health anxiety or fear of something worse is happening inside. This is the most frequent finding I see in my IBS patients).
Please read our complete guide about IBS and anxiety.
4- Pain and physical stress can trigger IBS flare-ups.
People with IBS may have much lower thresholds for pain (ref). Any physical stressor or painful condition can trigger a new IBS flare-up.
Common examples:
- Long working hours.
- Stressful or heavy gym exercises.
- Long travels.
- Running marathons
- Tooth pain.
- Trauma/bone fractures/ankle sprains or any painful condition.
- Simple infections such as influenza, common cold, and urinary tract infections can trigger IBS flare-ups.
5- Lack of adequate sleep.
A bad night’s sleep may result in a bad IBS day. Also, It is interesting to know that many people with IBS suffer from some form of sleep disturbance (ref).
So, try to obtain the optimum number of sleep hours (typically 7-8). You must change your sleeping behavior if you sleep less than 7 hours per night.
Also, irregular or random sleeping times due to work or travel may trigger your IBS flare-up.
6- Gut bugs can trigger IBS.
IBS flare-ups can be confused with actual gastroenteritis (especially IBS-diarrhea attacks).
Some Gut infections may resemble or trigger an IBS flare-up, such as:
- Viral gastroenteritis (stomach flu).
- Giardiasis.
- Food poisoning (foodborne illnesses).
- bacterial gastroenteritis
- Dysentery (amoebic and bacillary dysentery)
- and many others.
Sings it is a gut bug and not an IBS-flare up may include:
- Fever.
- Intense colics that are different from your usual previous IBS attacks.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Severe watery diarrhea or dysentery (unusual for your IBS type).
- Symptoms are severe, making you very ill with malaise or bony pains.
- Passage of bloody diarrhea.
And for sure, stomach bugs can add to your IBS and worsen your IBS flare-up (ref).
One of the strongest theories of IBS is the disturbance of your Gut Microbiota. Gut Microbiota are beneficial micro-organisms (mainly bacteria and fungi).
They live inside your gut and help to regulate digestion, absorption, intestinal motility, and immunity.
Disturbance in the intestinal microbiome ( as post-infectious IBS or post antibiotics may result in IBS.
Also, Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) may contribute to IBS. This is especially prevalent with IBS-diarrhea and IBS bloating.
We use some gut antibiotics to control IBS-Diarrhea attacks which may be caused by SIBO (ref).
7- Medications that can cause IBS flare-ups.
Check your list of medications; many of them can cause a new IBS flare-up by a variety of mechanisms:
- Killing the beneficial bacteria (microbiota) inside your colon: such as antibiotics (especially with prolonged use).
- Contains high FODMAP active ingredients such as cough syrups containing sorbitol.
- Containing high FODMAP inactive ingredients: sorbitol, xylitol, and others; for example, Advil gel capsules, can cause an IBS flare-up.
- Inducing colon hypermotility: some antidepressants, caffeine-containing medicines, Hormone-containing medicines, especially thyroid replacement hormones.
- Taking medications that can cause constipation or diarrhea: such as Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) such as Ibuprofen and Ketoprofen.
A rule of thumb is to check all the active and inactive ingredients of any medication you use. Review the list of drugs with your gastroenterologist.
8- Female Hormones and Menstruation.
Females are way more affected by IBS than males. This study estimates that females are affected by IBS up to 2.5 to 3 times more than males. And the number one cause of this may be your “female hormones.”
Any recent disturbance in your female hormones can act as a trigger for new IBS flare-ups.
That is why many IBS flare-ups in females occur during or before menstruation.
Also, some females may experience a change in IBS Flare-ups during pregnancy.
- Constipation attacks may increase during the third trimester of pregnancy.
- Some IBS patients also report more IBS-D flare-ups during their pregnancy.
Please read our Detailed article about IBS and Pregnancy.
The exact mechanism of female hormones is unclear. And the emotional alternations caused by female hormones may play a role in IBS flare-ups.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.







