IBS in Pregnancy: Risks & Best Treatments (GI Doctor Explains)
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
Pregnancy and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) can sometimes present similar symptoms, leading to confusion. In this article, we’ll delve into the symptoms of early pregnancy and IBS, highlighting their differences and overlaps.
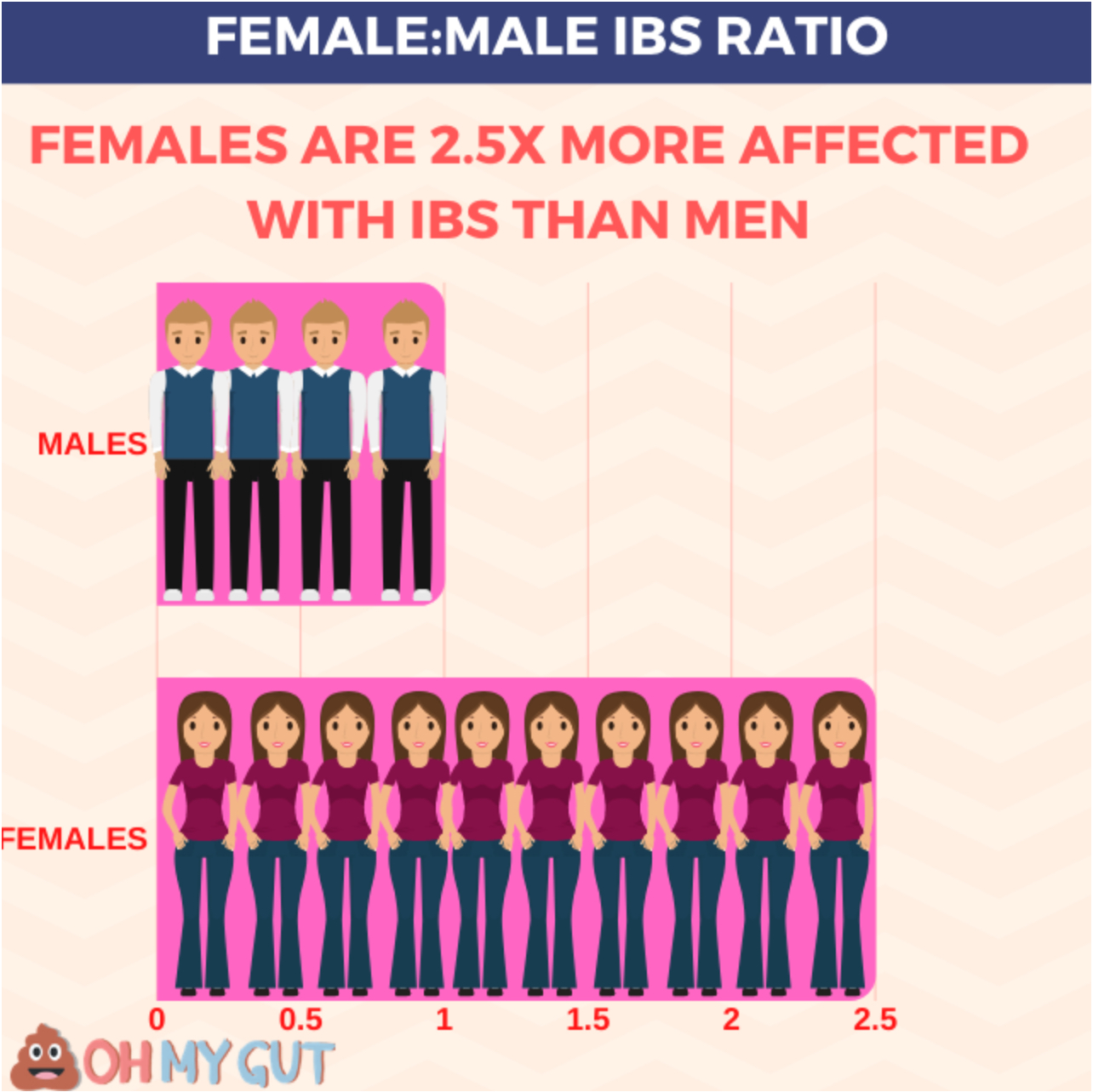
Females are 2.5 times more likely to experience IBS than men (reference). In pregnancy, IBS may cause further worsening in these symptoms. Keep reading for the best tips to beat IBS during pregnancy.
Key facts:
- Pregnancy and IBS can share similar symptoms, confusing.
- Early pregnancy symptoms can mimic menstruation signs.
- IBS symptoms can intensify during pregnancy.
- Pregnancy hormones may influence IBS symptoms.
- IBS symptoms can increase during the third trimester of pregnancy.
- IBS doesn’t prevent pregnancy but can be influenced by stress, which may impact fertility.
- IBS doesn’t typically cause problems during pregnancy, but severe cases need medical attention.
1- Differences between IBS and pregnancy symptoms.
Pregnancy symptoms in the early days can be confused with IBS symptoms. We will discuss the symptoms of early pregnancy and IBS symptoms and differences.
A- Symptoms of Early Pregnancy
Early pregnancy symptoms can vary greatly among women, with some experiencing severe symptoms, others having minimal signs, and some showing no symptoms at all. These symptoms can also resemble those of menstruation, making it challenging to identify pregnancy without a test.
In the early stages of pregnancy, you may experience:
- Mild cramps are similar to menstrual cramps, located in the lower abdomen, unrelated to meals, and unaffected by defecation.
- Morning sickness or nausea.
- Breast tenderness or soreness.
- Minimal spotting due to the implantation of the fertilized ovum in the uterus wall.
- Dizziness, possibly leading to fainting.
- Headaches and fatigue.
- Missed period.
B- Symptoms of IBS
If you have IBS, your symptoms may intensify after becoming pregnant. Typical IBS symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain in the form of colics and cramps, usually around the umbilicus and the lower left part of your abdomen.
- Pain that increases after meals and is related to defecation.
- Diarrhea, constipation, or both.
- Changes in stool form with the onset of IBS pain.
- Nausea and fatigue.
C- Can IBS Symptoms be Mistaken for Pregnancy?
IBS symptoms can be mistaken for early pregnancy signs due to their similarities. If you’re uncertain about your symptoms, consider taking a pregnancy test or consulting your doctor for a more accurate blood test (serum HCG).
2- Can Pregnancy Cause IBS Symptoms?
Pregnancy can potentially exacerbate IBS symptoms due to hormonal changes and the discontinuation of IBS medications. Hormones like Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG), progesterone, and estrogen increase during pregnancy and may influence IBS symptoms.
Another important cause that pregnancy may aggravate IBS symptoms is cutting off IBS medications. Most pregnant women cut off their IBS medication when they get pregnant. And this may cause more IBS flare-ups.
IBS and early pregnancy (first trimester).
The first trimester of pregnancy is the time for major changes inside your body. Your gut and your IBS are also affected. IBS may exacerbate in some pregnant females due to the above-mentioned factors:
- Hormonal changes occur with pregnancy.
- Cutting off your effective IBS medications due to safety issues with pregnancy.
But studies showed that the first trimester has fewer IBS symptoms frequency (compared to the third trimester):
The IBS symptom frequency according to each trimester are : (reference)
- 17% in the first trimester.
- 19% in the second trimester.
- 33.9% in the third trimester.
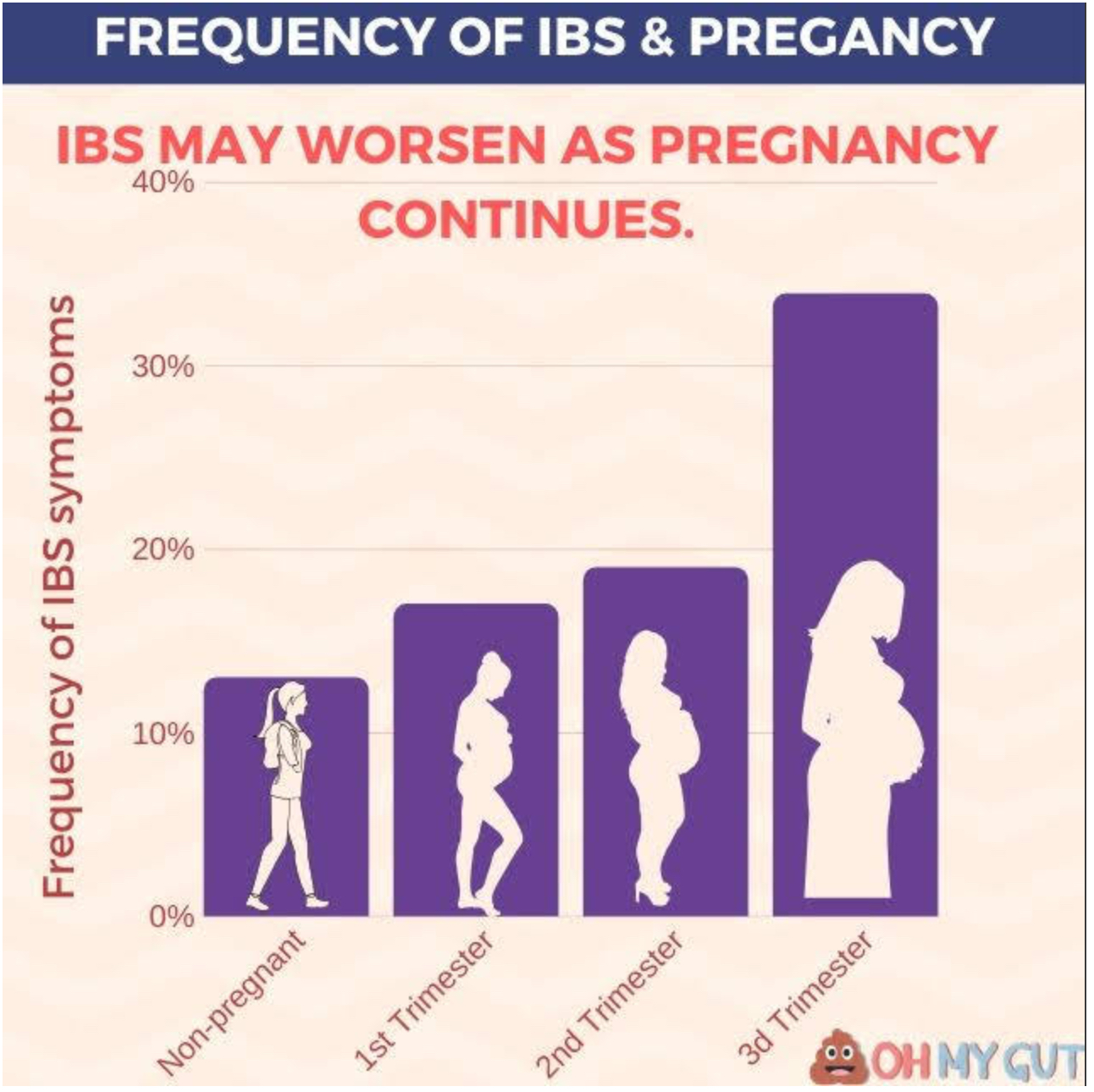
In the same study, the frequency of symptoms in non-pregnant women was 13%. This means that IBS symptoms in the first trimester may become slightly higher than before pregnancy (not in all females).
However, the difference was not big between pregnant and non-pregnant women.
IBS and late pregnancy (third trimester).
IBS may become worse during the third trimester. In this trimester, progesterone and estrogen levels are greatest. The progesterone hormone is known to slow things down inside your colon. However, both IBS-constipation and IBS-Diarrhea can occur during the third trimester.
In the third trimester, your baby grows, and the amount of amniotic fluid increases. This may cause IBS to get worse. Due to mechanical compression on your Gut and diaphragm, IBS bloating may also increase.
Also, you may get stressed in your late pregnancy as the delivery and arrival of your new baby become near. Stress can play a role in your IBS.
The most important concern is IBS-Constipation which worsens during the third trimester. You can relieve IBS constipation by the use of bulking agents and others (discussed later in this article).
MORE:9 Types of Lower Stomach Pain During Pregnancy Third Trimester.
3- Can IBS prevent you from getting pregnant?
There’s no scientific evidence suggesting that IBS can affect fertility. However, chronic stress and depression, often associated with IBS, can lead to Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea (FHA), which can cause fertility problems.
Chronic stress and depression in females can lead to Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea (FHA). FHA causes a disturbance in your menstrual period, and this may lead to fertility problems. (reference)
IBS itself is not known to prevent you from getting pregnant. But the same “stress” that led to IBS may lead to problems with fertility.
5- Can IBS affect or harm pregnancy?
IBS doesn’t typically cause problems during pregnancy, but severe IBS-diarrhea and IBS-constipation need medical attention. Some studies suggest a small increase in the risk of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy in women with IBS, but the evidence is still weak.
A large study [5] included about 100,000 pregnant women in the UK. Out of the 100k women, about 26k were diagnosed with IBS before pregnancy.
The study found a moderately increased risk of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy. But there was no risk of pre-eclampsia or stillbirth.
6- IBS relief during pregnancy (most effective tips).
Relieving IBS during pregnancy is quite a bit more challenging for you and your doctor. Some IBS medications are contraindicated during pregnancy.
I will mention the most effective tips to help you to cope with IBS during your pregnancy.what to do with IBS-D and IBS-C during pregnancy. And also, some details you should know about IBS medications and pregnancy.
(1) Avoid excess gas in your colon
With IBS and pregnancy, your colon may become more sensitive to gas, especially in the third trimester. Avoid gas-producing foods like beans, onions, celery, carrots, raisins, bananas, apricots, prunes, brussels sprouts, and carbonated beverages.
Also, avoid habits that can cause more gas in your colon, such as eating and swallowing food quickly, chewing gum, smoking, and remaining inactive after eating.
(2) Avoid FODMAP foods and fruits:
FODMAPs are a group of short-chain carbohydrates that your intestine cannot fully digest and absorb, leading to gas production. Gradually reducing your intake of FODMAP foods can help manage IBS symptoms.
- Fermentable: means that gut bacteria break them down, producing lots of gas.
- Oligosaccharides: Refers to compounds called fructans and galacto-saccharides present in wheat, barley, rye, onion, garlic, and legumes.
- Disaccharides: Refers to fructose sugar in milk, ice cream custard, and yogurt.
- Monosaccharides: Refers to free fructose present in Apples, pears, mangoes, cherries, watermelon, asparagus, sugar snap peas, honey, and high-fructose corn syrup.
- And
- Polyols: They are substances called sorbitol mannitol, xylitol, and maltitol, present in certain types of fruits like apples and watermelon and artificial sweeteners like artificially sweetened gum and alcohol.
(3) Gradually increase your fiber intake:
Fiber is a double-edged sword for IBS. Deficient fiber intake is thought to be a cause of IBS. On the other heading, eating too much fiber or increasing its amount too fast can hurt your IBS.
You should gradually increase the fiber intake, whether soluble (better for IBS) or insoluble.
Choosing the right type of fiber and its food source can be challenging. You can learn how to exactly eat fiber for IBS in our in-depth article: “Fiber and IBS”.
Also, if you have IBS constipation, you can consult your doctor about taking a safe fiber supplement like Psyllium.
(4) Manage your stress:
Physical and mental stress not only increase your IBS flare-ups but also may affect your pregnancy.
Simply, Understanding and accepting your IBS can help to relieve your pain. Try to:
- Talk about your conditions with your partner or close family members or friends. Just talking can relieve your stress and IBS.
- Do Yoga for IBS.
- Consult your doctor about CBT (Cognitive Behavioural Therapy) for IBS.
(5) probiotics are safe during pregnancy(reference])
In this Review article about probiotics and pregnancy, the authors concluded that probiotics are safe during pregnancy.
Although the scientific evidence for the use of probiotics is still not strong enough, we usually recommend a trial of a probiotic for IBS sufferers.
Probiotics (in some patients) can decrease IBS symptoms like gas, bloating, cramps, and diarrhea.
We suggest you try it for one month as it may be effective for you. For the best probiotics for IBS and how to take it, refer to this article.
7- Pregnancy and IBS-C management
The most effective and most safe strategies for managing your IBS-C are: (reference)
- Gradually increasing your dietary fibers (very effective). See how to eat fiber for IBS here.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Increase your daily exercise: for example, you can walk for 20 minutes twice a day after meals.
- Use safe laxative: A bulk-forming laxative like psyllium (Metamucil) may help you with constipation but consider using it for short-term periods.
Management of IBS constipation during pregnancy can be difficult. If the above tips don’t help, please consult your doctor.
8- Pregnancy and IBS-D management
If you have IBS-D, it’s crucial to drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration. Avoid trigger foods like FODMAPs and consider taking probiotics. If the diarrhea is mild, it often resolves itself within a few days. However, consult your doctor if you’re unsure about the cause of your diarrhea or if it’s severe.
C- IBS medications during pregnancy.
Many drugs are used for IBS, and their safety during pregnancy varies. Discuss any medication or supplement you’re taking for IBS with your doctor during pregnancy.
Some of the over-the-counter drugs and supplements are not considered safe during pregnancy. The below table summarizes the pregnancy category of each IBS medications and its safety with pregnancy: [8]
- Category A drugs: studies showed that the drug is safe for the fetus.
- Category B drugs: studies on animals showed that the drug is safe, but no controlled human studies.
- Category C drugs: No controlled studies have been done on animals or humans. Potentially unsafe.
- Category D drugs: evidence of risk to fetus presents. But can be taken in dangerous or life-threatening conditions.
- Category X drugs: strong evidence of risk in both animal and human studies. Its risks outweigh any benefits.
- N: Not classified by FDA
You can find the full list of IBS drugs and their pregnancy category at Drugs.com.
ALWAYS WORK WITH YOUR DOCTOR TO SELECT THE BEST TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR YOUR PREGNANCY.
FAQs about pregnancy and IBS:
Can IBS affect the baby when pregnant?
IBS itself does not directly affect the baby during pregnancy. However, severe symptoms of IBS, such as diarrhea, can lead to dehydration, which can potentially affect the baby. It’s important to manage IBS symptoms effectively during pregnancy and stay hydrated.
Does IBS cause miscarriage?
There’s no strong scientific evidence to suggest that IBS can cause miscarriage. However, a large study did find a moderately increased risk of miscarriage in women with IBS. The evidence is still weak, and the risk is small. Always consult with your healthcare provider if you have concerns.
We’re talking about a 2012 study that concluded that IBS might increase the risk of miscarriage. The study with done on a large group (100,00 women). However, the risk of miscarriage was only slightly higher. Read the study.
Can you develop IBS during pregnancy?
While it’s possible for the symptoms of IBS to first appear during pregnancy due to hormonal changes and increased stress, it’s more common for women who already have IBS to experience a change in their symptoms during pregnancy. If you’re experiencing new gastrointestinal symptoms during pregnancy, discussing them with your healthcare provider is important.
Can pregnancy cause postpartum IBS?
Pregnancy doesn’t directly cause postpartum IBS, but the hormonal changes and physical stress of pregnancy can trigger IBS in some women. Additionally, the stress of caring for a new baby can also trigger IBS symptoms. If you’re experiencing persistent gastrointestinal symptoms after giving birth, discussing them with your healthcare provider is important.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.

Related Posts:
- Can You Get Norovirus Twice? Doctor Explains the…
- Liver Pain in Females: Location, Causes, Pregnancy, & More.
- Impacted Stool: Treatments & Best Laxative, A…
- How To Diagnose IBS (Simplified + Quiz), Doctor Explains.
- Does Ibuprofen trigger or relief IBS? GI doctor Explains
- IBS pain relief: 8 Most Effective Tips From A Doctor…







