Fluffy Poop: 7 Causes & When to Worry (Doctor Explains).
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
Table of Contents
What does fluffy poop mean?
People often use the term fluffy to describe mushy or loose stool with fuzzy coating due to high fiber, mucus, or fat in the stool.
Fluffy stools are often more loose than normal and contain more water, fibers, mucus, or fat.
Fluffy poop is not a specific medical condition; it is a sign that can result from a variety of dietary factors, diseases, or medications.
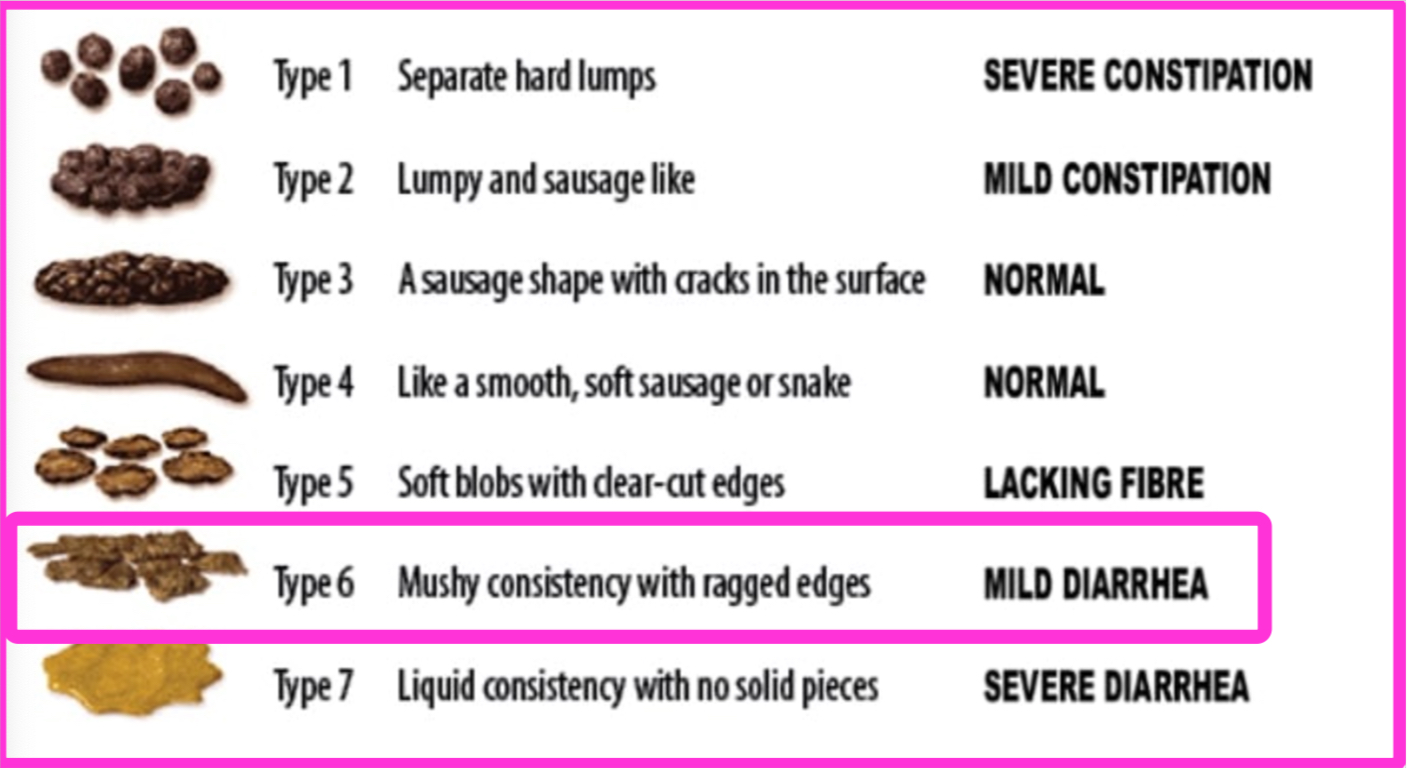
Fluffy poop may be called type 6 stool on the Bristol Stool Form Score (BSFS) Chart, an objective method that helps doctors determine the stool’s form.
Type 6 in the Bristol Stool Form Scale is Mushy or fluffy with ragged and torn edges (like fluff).
Also, the fluffy or fuzzy coating on the stool can occur with Type 5 and type 7.
Fluffy stools can be either:
- Acute: sudden onset of loose, fuzzy stools with a fluffy coating of mucus or fiber.
- Chronic: when you experience fluffy poop every day for a prolonged period of time.
- Intermittent (occasional) fluffy poop every few days, weeks, or months. The poop returns to normal in between the attack.
Fluffy poop causes.
Fluffy poop can be caused by different diseases and conditions. The most common cause include lactose intolerance, irritable bowel syndrome, and other food intolerances and allergies.
Infections (acute and chronic) and medications are common causes of soft fluffy poop that disintegrates in water or floats in the toilet.
Below is a breakdown of the common causes of fluffy poop:
1. Lactose intolerance.
Lactose intolerance is the inability to digest lactose (the chief sugar in milk and dairy products).
Lactose intolerance is extremely common, and you may have it without knowing. 30 to 50 million Americans are lactose intolerant in the USA.
Lactose intolerance is even more common in certain races and countries. 80% of African American people are lactose intolerant.
You will experience diarrhea, loose stool, or fluffy poop daily when you drink milk or eat lactose-containing dairy products.
Symptoms:
The symptoms are related to lactose ingestion. It may be chronic or intermittent based on your eating habits.
- Abdominal pain.
- Bloating.
- Distension and excessive passing of gas.
- Nausea.
- Diarrhea may or may not be present.
- The stool often becomes soft, fluffy, or watery. Also, it is yellowish or pale in color and may float in the toilet.
- In children, the stools are bulky, frothy, and watery. Vomiting is common among adolescents with lactose intolerance.
2. Infection (dysentery and gastroenteritis).
Infections of the gastrointestinal tract often lead to speeding up the intestinal and colon content, resulting in a soft, fluffy poop that may progress to watery stool.
Gut bugs such as viruses, bacteria, and protozoa may invade your small intestine and the colon causing digestive symptoms such as diarrhea with mucus discharge (a white fluffy substance in stool), abdominal pain, and flatulence.
A dysentery is a special digestive system infection that predominantly affects the colon and the rectum. Dysentery is often characterized by the passage of mucus only stools (fluffy mucus discharge), blood in stool, extreme urge to defecate, and
Any infection can cause increased mucus in poop which can be white or colored (yellowish).
For Example:
- Acute viral gastroenteritis (stomach flu).
- Acute dysentery (can lead to mucus-only poop).
- Most types of foodborne illnesses (food poisoning).
- Also, chronic causes of intestinal infections can lead to white mucus in poop.
Symptoms of acute viral gastroenteritis (stomach flu):
- Most often, acute infections cause acute onset diarrhea with mucus discharge (loose or watery stool with mucus).
- Abdominal pain (Belly pain).
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Lowgrade fever and body aches.
- Chronic infections, prolonged mucus in stool, diarrhea, and abdominal pain are frequent symptoms.
Symptoms of Dysentery:
- Severe, frequent attacks of diarrhea.
- The diarrhea is mixed with mucus, blood, or both. Mucus often appears as a white fuzzy or fluffy substance in poop.
- Extreme urgency to poop.
- In severe cases, mucus discharge comes out without stool.
- Abdominal pain.
- Fever (it can be of high grade).
3. Irritable bowel syndrome.
Irritable bowel syndrome is a widespread and underdiagnosed condition. at least 10-15% of the entire population have IBS.
The disease alone represents 40% of Gastroenterologist clinic visits in the USA.
It is a functional disease (unclear cause) that leads to chronic or recurrent abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and bowel habit changes. Fluffy poop and gas are common in patients with IBS.
Symptoms of IBS:
- Abdominal pain that is recurrent at least one day per week (for several months).
- The pain improves or worsens after bowel movements.
- The pain is associated with a change in stool form (becoming loose, fluffy, watery, or hard).
- The pain is associated with a change in stool frequency (diarrhea or constipation).
- All the symptoms come and go intermittently in attacks (including on-and-off diarrhea and mucus discharge).
- Triggers are usually food and psychological stress.
- Flatulence, particularly after consumption of a high-FODMAP food.
- Mucus discharge is one of the features of IBS according to the manning criteria for IBS diagnosis.
Patients with Irritable bowel syndrome are often sensitive to a group of foods collectively called the FODMAPs (Fermentable oligo-, Di-, Monosaccharides, and polyols.
Characteristics and sources of common FODMAPs
| Sugar type | Foods containing | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| F | Fermentable | ||
| O | Oligo-saccharides | Fructans, galactooligosaccharides | Wheat, barley, rye, onion, leek, the white part of spring onion, garlic, shallots, artichokes, beetroot, fennel, peas, chicory, pistachio, cashews, legumes, lentils, chickpeas |
| D | Di-saccharides | Lactose | Milk, custard, ice cream, and yogurt |
| M | Mono-saccharides | “Free fructose” (fructose in excess of glucose) | Apples, pears, mangoes, cherries, watermelon, asparagus, sugar snap peas, honey, high-fructose corn syrup |
| A | And | ||
| P | Polyols | Sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, and xylitol | Apples, pears, apricots, cherries, nectarines, peaches, plums, watermelon, mushrooms, cauliflower, artificially sweetened chewing gum, and confectionery |
4. Other forms of food intolerance & allergy.
Food intolerance occurs when your gut has trouble digesting or absorbing certain types of food or food component.
As a result, the undigested and/or unabsorbed foods remain longer inside your intestines.
Bacteria then consume the stagnant food and produce extra gas (even with average amounts of food).
The more you eat the offending foods, the more you will get flatulence and other digestive symptoms such as loose or fluffy stool, diarrhea, and mucus.
Food intolerance is widespread, affecting up to 20% of people.
Food intolerance is different from food allergy. Food allergy is an allergic reaction to food (mediated by your immune system).
The symptoms of food intolerance are identical to lactose intolerance symptoms (explained above). The only difference is the trigger food.
Common forms of food intolerances:
- Lactose intolerance (explained above).
- Fructose intolerance: a sugar present in most types of fruits and honey.
- FODMAP intolerance.
- Amines intolerance.
- Caffeine intolerance.
- Alcohol intolerance.
- Salicylates intolerance.
5. Medications that may cause fluffy poop
Medication is another leading cause of stool changes, including loose and fluffy stool.
More than 700 medications can lead to loose fluffy stool or diarrhea.
Always review your list of medications to determine if the fluffy poop is caused by one or more.
Common medications:
- Metformin is a widely used anti-diabetes medication and is considered the first-line therapy for new cases. Metformin-induced diarrhea is a very frequent side effect of the drug. Check your anti-diabetes tables, as they can be the source of unexplained diarrhea.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotic-associated diarrhea is a frequent side effect of taking antibiotics. Antibiotics cause the death of beneficial microbes inside your gut, disturbing digestion and allowing other harmful organisms to grow. Common antibiotics to cause such conditions are Penicillin, cephalosporins, and clindamycin antibiotics.
- Gastritis and GERD medications: – Proton Pump Inhibitors such as Esomeprazole (Nexium), Pantoprazole (Protonix), and Omeprazole (Prilosec). – H2 blockers such as Famotidine and Ranitidine (Zantac).
- Cancer chemotherapy:
- Immunosuppressive medications: These medications treat immune-mediated diseases such as Systemic Lupus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura, and others. Examples include Mycophenolate and Methotrexate.
- Furosemide (Lasix): A famous diuretic medication is used in various diseases, especially in people with heart disease.
- Chronic laxative abuse.
For the complete list, Learn more HERE and HERE.
6. Celiac disease.
Celiac disease affects about 1% of the population. It causes severe intestinal inflammation and malabsorption after eating gluten.
Gluten is a protein found mainly in wheat, rye, and barely. Eating wheat-based food triggers celiac disease symptoms, including fluffy poop or diarrhea.
Symptoms of celiac disease:
- Chronic diarrhea or loose stool (fluffy poop).
- Sometimes, constipation also occurs.
- Bloating and gas.
- Nausea, loss of appetite.
- Weight loss.
- Anemia (can be severe if left untreated).
- Abdominal pain.
- In rare cases, it can cause constipation.
Learn more about stool changes in celiac disease.
7. Inflammatory bowel disease.
More than 1.6 million Americans suffer from inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), a chronic gut inflammation of unclear cause.
Inflammatory bowel disease leads to chronic diarrhea, loose or fluffy stools, and bloody mucus discharge.
The disease leads to inflammation and ulceration of the colon (ulcerative colitis), or it may present as widespread ulceration and inflammation affecting the entire gastrointestinal tract (Crohn’s disease).
Symptoms of IBD:
- Persistent or recurrent diarrhea or soft fluffy poop.
- Abdominal pain.
- Blood or blood and mucus coming out with or without a stool.
- Weight loss.
- Generalized fatigue.
- Fever may occur.
- Loss of appetite.
Suspect IBD if you have a prolonged history of abdominal pain, mucus, and blood in stool without obvious cause.
For doctors to diagnose IBD, they usually need to perform a colonoscopy. A colonoscopy will help visualize the lesion, and your endoscopist may take a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. (reference
Here are the main differences between Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis:
| Type | Crohn’s Disease | Ulcerative Colitis |
|---|---|---|
| 1- Site | Any part of the GI tract (from the mouth to the anus) | The large intestine (colon). |
| 2- Lesions | Deeper, it can involve all the layers of the GI wall. | Usually superficial (only in the innermost layer) |
| 3-Predominant symptom | Crampy abdominal pain | Bloody diarrhea. |
| 4- Complications | Fistulas, abscess, intestinal obstruction | Hemorrhagic and toxic megacolon. |
| 5- Risk of colon cancer | Slight increase | Marked increase |
8. Other (less common):
- Diabetes mellitus (autonomic neuropahty).
- SIBO (small intestinal bacterial overgrowth).
- Post-cholecystectomy syndrome and bile acid diarrhea.
- Stress and anxiety.
- FODMAP intolerance.
- Colorectal cancer.
- Mesenteric ischemia
- Chronic pancreatitis (Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency).
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Radiation colitis.
- Microscopic colitis.
- Sarcoidosis.
- Addison’s disease.
- Chronic liver diseases such as liver cirrhosis.
- Neuroendocrine tumors such as carcinoid syndrome and VIPoma.
- Rare intestinal diseases such as
When to worry about fluffy poop?
Occasional loose or fluffy stool without other symptoms, such as abdominal pain, is often due to dietary or lifestyle changes. Also, it may be due to widespread conditions such as lactose intolerance which affects most adults.
However, you should also talk to your doctor if you persistently have loose or fluffy stools for a long period.
See a doctor if you have the following:
- Persistent fluffy stool for several weeks or months (with or without mucus).
- Severe diarrhea.
- Fluffy stool and blood.
- Fluffy stool and excessive gas and indigestion.
- Significant abdominal pain.
- Fever.
- Intense nausea or vomiting.
- Unexplained weight loss.
FAQ.
What causes fluffy poop and gas?
The most common causes of fluffy poop and gas are food intolerances such as lactose intolerance, irritable bowel syndrome, and infections (gut bugs). Other less common causes include celiac disease, IBD, and medications.
What causes fluffy poop and stomach pain?
Common causes of fluffy poop and stomach pain include:
- Faulty diet habits include eating too many vegetables, fats, or fruits.
- Food intolerances such as lactose intolerance.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Infections such as gut viruses and parasites.
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
- Celiac disease.
- Others, such as SIBO, medications, etc.
What causes fluffy poop with mucus?
Common causes of fluffy poop with mucus include food intolerances (such as lactose intolerance), Dysentery, Inflammatory bowel disease, and irritable bowel syndrome.
What causes fluffy poop every day?
Chronic fluffy poop every day is often a reflection of a chronic digestive condition such as irritable bowel syndrome, lactose intolerance, celiac disease, or inflammatory bowel disease. Always consult your doctor if your stool form is always loose or fluffy.
What causes fluffy poop and blood?
Causes of fluffy poop and blood include dysentery, inflammatory bowel disease, and local rectal conditions (proctitis, fissures, piles). It can also result from a serious condition such as colorectal cancer. Always consult your doctor if you have significant blood in your stool with fluffy poop.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.