Bloating after Colonoscopy: Causes & How to Relieve it.
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
Bloating is the visible distension of your abdomen, with or without a sense of fullness. It is the most common side effect of colonoscopy (reference).
Being bloated after colonoscopy can be due to many factors. However, the most impactful factor is the use of gas to inflate your colon during a colonoscopy.
Bloating is often benign and not a sign of complication. Usually, you won’t need to see a doctor unless you have warning signs (discussed later).
The infographic below illustrates the frequency of post-colonoscopy symptoms, with bloating being the commonest.
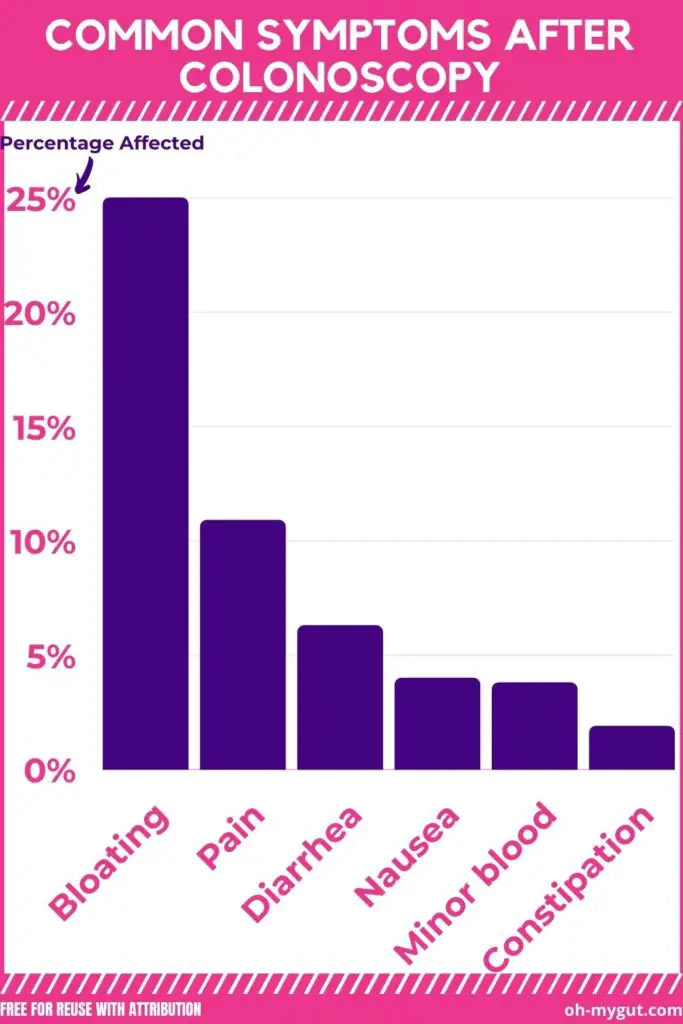
1. Trapped gas after colonoscopy.
The colonoscopy pumps gas (air or Carbon dioxide) to inflate your colon. This helps the colonoscopist to perform colonoscopy and visualize any lesions.
Your colonoscopist typically tries to deflate air from your colon as he pulls the colonoscope out. However, the process is not optimum, and you often will be left with excess gas inside your colon after colonoscopy.
The trapped gas after colonoscopy is the most common cause of bloating after colonoscopy.
Prolonged bloating due to trapped gas can be due to other factors as eating fatty or fried food after colonoscopy, lack of activity, or anesthetic medication. However, more often, bloating is multifactorial and not due to a single factor.
Treatment
The bloating from trapped gas often resolves spontaneously within hours to a day or two after colonoscopy.
Part of the trapped gas passes out with flatus, and another part is absorbed into the bloodstream.
You can fasten the gas release from your colon by:
- Early mobilization and activity help to regain your colon motility.
- Abdominal massage with a circular motion and gentle pressure over your belly to help gas release.
- Eat smaller meals and avoid fatty and fried food in the first couple of days after colonoscopy.
- Take anti-flatulent capsules such as peppermint or simethicone.
- Don’t ignore the need to defecate or to pass flatus.
2. Colonoscopy preparation.
Colonoscopy preparation is a strong laxative that is used to empty your colon before a colonoscopy.
Colonoscopy preparation induces severe diarrhea with fluid and electrolyte loss during the period before colonoscopy.
This preparation may cause gastrointestinal disturbances such as abdominal pain and bloating after colonoscopy.
The most significant side effect of colonoscopy preparations is electrolyte disturbances. Electrolyte disturbances (such as loss of potassium or sodium) affect the motility of your colon.
Persistent diarrhea after colonoscopy may indicate a preparation after-effect. However, the resulting bloating often resolves with good rehydration and proper eating.
Most often, The bloating is mild with no other complications. Bloating then will resolve on its own as your colon reverts gradually to its original condition.
3. Anesthesia after-effects.
Anesthesia is commonly used during a colonoscopy. It ranges from light sedation to general anesthesia.
Anesthesiologists use a famous group of medications called (opioids). Opioids are famous for slowing your colon contractions.
Opioid medications (such as morphine, fentanyl) commonly cause constipation and bloating after colonoscopy.
New-onset constipation and bloating after colonoscopy can be a side effect of the anesthetic medications you take.
The condition often resolves gradually as your body gets rid of the medication within a few days.
If bloating is associated with severe constipation taking a stimulant laxative (such as Dulcolax) can improve the condition. Consult your doctor about the available options.
4. Procedures during colonoscopy.
Procedures that cause pain or mild inflammation during colonoscopy can result in bloating.
Removing a polyp, taking a biopsy, or ligating hemorrhoids can lead to local inflammation in the colon wall. This can trigger abdominal pain, constipation, or bloating.
Bloating from painful procedures is frequent. However, it is expected to resolve over time as the pain and inflammation decrease.
5. Exacerbation of the original disease.
Mostly, you have an acute or chronic colon disease or condition that led you to colonoscopy.
Sometimes, the original colon disease (for which the colonoscopy was done) can cause bloating after colonoscopy.
For example:
- Ulcerative colitis.
- Crohn’s disease.
- Irritable Bowel syndrome.
- Diverticular disease.
- Chronic constipation.
- Colon tumors (benign or malignant).
- Food intolerance or allergy.
- Malabsorption syndromes.
All the above conditions can indicate your colonoscopy and the cause of post-colonoscopy bloating at the same time.
Moreover, The colonoscopy preparation and the colonoscopy procedure can act as triggers to the original condition. The combination of these factors ends in bloating after colonoscopy.
As a result, the treatment of bloating is directed towards the treatment of the original disease.
6. Faulty eating and drinking habits after colonoscopy.
Overeating unhealthy or gassy foods after colonoscopy can ultimately lead to bloating after colonoscopy.
Early eating before your colon resumes its normal motility can also lead to bloating.
The list of food that commonly causes gas and bloating include (reference):
| 1. Milk and dairy products | – milk, – ice cream, – and sometimes, cheese and yogurt. |
| 2. Vegetables | – Broccoli, – cauliflower, – Brussel sprouts, – onions, – leeks, – parsnips, – celery, – radishes, – asparagus, – cabbage, – kohlrabi, – cucumber, – potatoes, – turnips, – and rutabaga. |
| 3. Fruits | – Prunes, – apricots, – apples, – pears, – peaches, – raisins, – bananas |
| 4. Whole grains | -wheat, – oats, – bagels, – wheat germ, – pretzels, – bran/bran cereal |
| 5. Legumes | – Beans, – peas, – baked beans, – soybeans, – lima beans |
| 6. Fats | Fried and high-fat foods. |
| 7. Drinks | – Carbonated beverages, – beer, – carbonated medications |
| 8. Others | – chewing gum, – artificial sweeteners |
The essential foods that cause bloating after colonoscopy are fatty foods and carbonated beverages.
8. Rare But severe causes of bloating after colonoscopy.
Isolated bloating without other severe symptoms is often a mild side effect. However, bloating after colonoscopy can be a sign of complication such as:
- Colonoscopy-induced colon perforation.
- Post-polypectomy coagulation syndrome.
- Infection.
The complications of colonoscopy don’t present with isolated bloating. Instead, it often consists of a complex of red flag symptoms and signs such as:
- Fever.
- Severe abdominal pain and tenderness.
- Passage of blood in the stool.
- Persistent vomiting.
- Dizziness, general ill feeling, and fast heartbeats.
- Sometimes, fainting and loss of consciousness.
See a doctor immediately if you experience one or more of the above symptoms after colonoscopy.
Tips on treating bloating after colonoscopy:
- Avoid the early and over-consumption of foods and drinks such as fatty foods and carbonated beverages.
- Move early and avoid prolonged bed stay after colonoscopy.
- Don’t ignore the need to pass flatus or poop after colonoscopy.
- Start with small meals and don’t overeat in the early period after colonoscopy.
- Use peppermint tea or peppermint capsule supplement.
- Simethicone is an OTC anti-flatulent and anti-bloating agent that helps with bloating after constipation.
- Consult your doctor for better evaluation and decision about what works for you.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.






