Pain in the Middle of Stomach Above Belly Button: 9 Causes, Gastroenterologist explains.
Our content is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice by your doctor. Use for informational purposes only.
Possible causes of stomach pain in the middle above the belly button include:
- Gastritis.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Functional dyspepsia.
- Gallbladder diseases such as gallstones and acute cholecystitis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Gastroparesis.
- Others: such as IBS, IBD, liver diseases, and cancers.
To know what is your specific cause, read the in-depth explanation below.
An MD writes this article on gastroenterology and hepatology. However, it is not a replacement for medical advice and evaluation by your doctor.
1 . Gastritis.
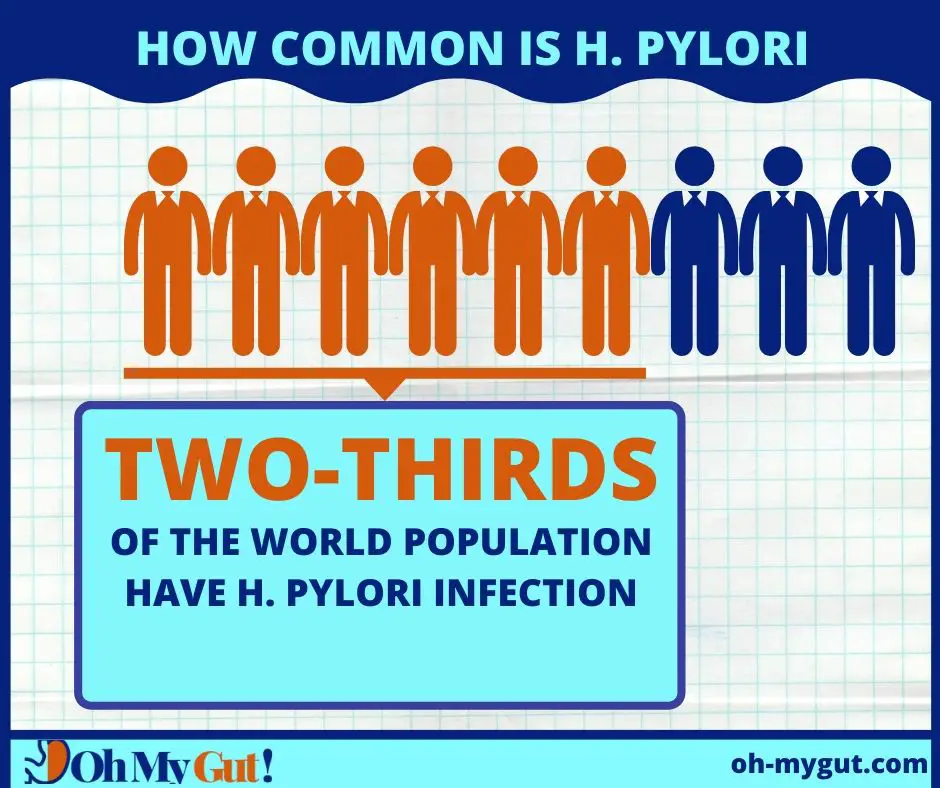
Gastritis is the inflammation of your stomach lining. Gastritis is very common. The Vast majority of gastritis is due to a widespread stomach bug called H. pylori.
H. pylori is a widespread infection, particularly in developing countries. It affects around two-thirds of the world’s population (reference).
Gastritis can be acute or chronic when the upper stomach pain is prolonged.
Causes of gastritis (reference):
- H. pylori infection.
- Analgesic abuse (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Other medications: such as iron supplements, some antibiotics, and corticosteroids.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Autoimmune gastritis: an immune-mediated disease. It mainly affects younger women. Autoimmune gastritis leads to atrophy of the stomach lining and malabsorption of iron and vitamin B12 leading to anemia.
- Bile acid reflux.
- Less common causes: radiation, autoimmune diseases, Crohn’s disease, and others.
Symptoms:
- Pain in the upper middle stomach above the belly button (epigastric area). The pain is often located just below the rib cage in the middle.
- The character of pain: burning, gnawing, or dull aching continuous pain.
- Triggered by: eating, particularly acidic, spicy foods and caffeinated drinks.
- The pain is often associated with nausea or vomiting.
- Fullness in the middle of the stomach after eating.
- The pain often improves with anti-acid treatments such as antacids, H2 blockers (such as famotidine), or proton pump inhibitors (such as omeprazole).
2. Peptic ulcer disease.
Peptic ulcer disease is often a complication of chronic gastritis. H. pylori and Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the two most common causes of peptic ulcer disease.
A peptic ulcer affects either your stomach or your duodenum. Stomach and duodenal ulcer symptoms are similar to gastritis symptoms. But they can become complicated.
The two most important complications of peptic ulcer disease are:
- First, bleeding (leads to vomiting blood and passage of blackish stool).
- Perforation: the ulcer leads to a hole in the wall of your stomach or duodenum. It is often an emergency medical condition with extreme abdominal pain and tenderness.
Both stomach and duodenal ulcers cause stomach pain above the belly button (umbilicus). The differences between stomach ulcer and duodenal ulcer symptoms are illustrated in the table below.
| Items | Gallbladder pain (biliary colic). | Peptic ulcer pain |
| 1. Site (typical) | Right-upper abdomen. | Mid-upper abdomen (epigastric) |
| 2. Spread) | To the right-back and the epigastric area. | Sometimes, to the mid-upper back. |
| 3. Character | Constant. It builds up over 30-60 minutes and then resolves gradually. | Constant gnawing or dull aching pain. Starts gradually and may last for several days. |
| 4. Duration | – At least 30 minutes. – Maximum is 6 hours. | Several hours to several days or weeks. |
| 5. Pain intensity | +++++ | +++ or ++++ |
| 6. Nausea & vomiting | +++ | ++ |
MORE: How Frequent is Back Pain with Duodenal Ulcers?
3. Functional dyspepsia (FD).
Functional dyspepsia (indigestion) is a widespread condition. In addition, FD is a common cause of middle stomach pain above the belly button.
Functional dyspepsia affects up to 5-11% of people without apparent cause (reference).
Symptoms: (reference):
- Pain or discomfort in the middle of the stomach area above the belly button.
- Early satiety soon after you start eating.
- A sense of fullness in the upper-middle part of your abdomen after eating.
- Epigastric (upper-middle abdomen) burning.
- Bloating after eating.
- Excessive belching.
- Nausea can also be present.
The above symptoms are non-specific and can occur with chronic gastritis. The differentiation without the help of your doctor is impossible.
The differences between functional dyspepsia and gastritis are:
- First, the pain is less severe (usually in discomfort).
- The sense of fullness and bloating after eating.
- Your doctor has to exclude gastritis by performing an endoscopy exam of your stomach and duodenum.
4. Gallbladder diseases.
Your gallbladder can cause pain above the belly button, either to the right side or in the middle of the stomach.
Causes of gallbladder pain:
- A stone inside your gallbladder (gallstone).
- Obstruction and inflammation of the gallbladder (acute cholecystitis).
- Functional gallbladder disease.
- A stone inside the bile ducts (cholelithiasis).
- Gallbladder polyp or tumor.
Gallbladder pain can mimic gastritis and peptic ulcer disease.
Symptoms of gallbladder pain:
The summary of characteristics of gallbladder pain is in the below table. Typical gallbladder pain is often due to uncomplicated gallstones.
| Biliary colic (Uncomplicated gallstone). | Description |
| 1. Site | Usually, The right upper quadrant of your abdomen |
| 2. Spread | – The pain may spread to the back of the right shoulder. – Also, it spreads to the epigastric area. |
| 3. Character | Constant builds up then disappears gradually. |
| 4. Duration | At least 30 minutes. It may last up to 6 hours. |
| 5. Relation to food | – Triggered by foods (especially fatty food and large meals. – However, it can start spontaneously. |
| 6. NOT related to: | Movement, bowel movements, nor the passage of flatus. |
| 7. Nausea | Often Present, severe. |
| 8- Commonly associated symptoms | Vomiting, sweating during the attack. |
| 6. Unusual symptoms. | – Heartburn and chest pain. – Bloating, fullness. – Early satiety. – Isolated epigastric pain. |
| 6. Symptoms NOT associated: | – Fever. – Jaundice. – Prolonged pain for more than 6 hours. – Extreme tenderness over the gallbladder (Murphy’s sign). – Vomiting of blood, blackish stool (PUD). |
Gallstones may lead to the obstruction of the gallbladder outflow leading to acute cholecystitis (prolonged gallbladder pain and fever).
In addition, gallstones may slip and obstruct the common bile duct leading to jaundice, dark urine, and clay stool.
Learn more about the mimics of gallbladder pain.
5. Gastroparesis.
Gastroparesis occurs when your stomach takes more time to empty its contents. It is often due to the inability of your to move and propel food.
Causes:
- Unknown: about 50% of the cases of gastroparesis are of unknown cause.
- Diabetes mellitus: prolonged diabetes mellitus is a significant risk factor for gastroparesis (Diabetes affects the nerves supplying your stomach).
- Viral stomach infections (such as norovirus and rotavirus). These viruses cause acute gastroparesis.
- Some medications: some antihypertensive medications, tricyclic antidepressants, Clonidine, some anti-diabetes drugs, and more.
- After surgery: some abdominal and chest surgeries cause damage to the stomach nerve supply (the vagus nerve).
- Some neurological diseases as multiple sclerosis (MS), brain stem stroke, and Parkinson’s disease.
Symptoms:
- E prolonged sense of fullness after eating.
- Discomfort or stomach pain in the middle above the belly button.
- Nausea (93%)
- Vomiting (Up to 84%)
- Early satiety (Up to 86%)
- Fullness after meals, bloating.
- Weight loss in severe cases.
Learn More about gastroparesis.
6. Pancreatic diseases.
Pancreatitis pain is often in the upper-middle stomach area (above the belly button). The pancreatic pain is often severe.
The various diseases of the pancreas can lead to such pain. The most common causes are:
- Acute pancreatitis.
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Pancreatic cancer.
Gallstones are among the most common causes of acute pancreatitis (they obstruct the pancreatic duct). Also, alcohol abuse is among the most common causes of chronic pancreatitis.
Symptoms of pancreatitis:
Acute Pancreatitis:
- Acute onset, severe, persistent pain in the upper middle stomach (above the belly button).
- The pain may be in the right upper part of your stomach.
- Nausea and vomiting are present in about 90% of the causes (reference).
- The pain radiates to the back (upper mid-back area) in 50% of the cases (reference).
- Shortness of breath.
- Fever.
Chronic pancreatitis:
- Pain above the belly button in the middle of the stomach (less severe than acute pancreatitis pain).
- The pain often radiates to the back.
- Recurrent diarrhea, particularly after eating fatty foods. The stool is yellowish or grey, with an oily consistency.
- Weight loss.
- Occasional nausea or vomiting.
- Some patients are asymptomatic.
7. Others.
The list of the causes below is either:
- Uncommon or rare.
- Common but less likely to cause pain above the belly button.
Other causes may include:
- Irritable bowel syndrome and Inflammatory bowel disease: the two disease affects the colon primarily, with the tendency to cause diffuse abdominal pain rather than middle stomach pain above the umbilicus.
- Food intolerance and allergy: often associated with diarrhea, bloating, and distension.
- Coronary artery disease: Atypical forms of ischemic heart disease may present with upper-middle stomach pain without chest pain.
- Cancers: stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer, liver cancer, gastric lymphoma, colorectal cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and biliary system cancer (cholangiocarcinoma).
- Liver diseases: hepatitis, liver abscess, liver hemangiomas, liver cirrhosis, and others.
- Abdominal wall hernia (epigastric hernia): often associated with a swelling in the middle of the stomach above the belly button.
- Abdominal muscle strain: Usually, the pain is associated with movement.
When to see a doctor?
Stomach pain in the middle above the belly button is often due to mild conditions such as functional dyspepsia or mild gastritis.
See a doctor if:
- Prolonged undiagnosed abdominal pain.
- Acute severe (intolerable) stomach pain.
- High-grade fever.
- Frequent vomiting.
- Blackish stool or vomiting of blood.
- Dark urine (tea-colored), yellowish eye whites, or yellowish skin).
- Severe tenderness on touching your abdomen.
- Dizziness, shortness of breath, or unexplained chest pain.
- Evidence-based
- Written by a doctor.